Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
galloylpedunculagin overhangs the H-5 of another molecule. The low-
field shift observed for the 2,3-HHDP pyrogallol ring proton can be
rationalized in terms of a deshielding effect induced by the O-1 galloyl
group of another molecule. Interestingly, if an oxidative coupling
between these galloyl and hexahydroxydipenoyl groups occurred
according to the C-C coupling mode A, it would give rise to
rhoipteleanin A (see Fig. 4.8), a major dimeric ellagitannin isolated from
Rhoiptelea chiliantha
(Jiang
et al.
, 1995).
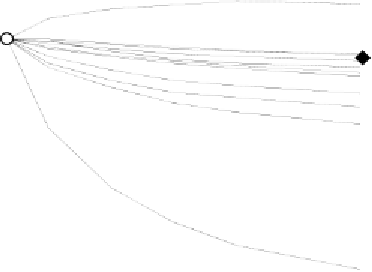
0.10
0.05
HHDP-H attached to glc C-2
0.00
-0.05
-0.10
Δδ
-0.15
-0.20
-0.25
-0.30
glucose H-5
-0.35
-0.40
0
0.005
0.01
0.015
0.02
0.025
0.03
0.0014M
[M]
Galloyl
HHDP(6)
HHDP(4)
HHDP(2)
HHDP(3)
Glc-1
Glc-3
Glc-2
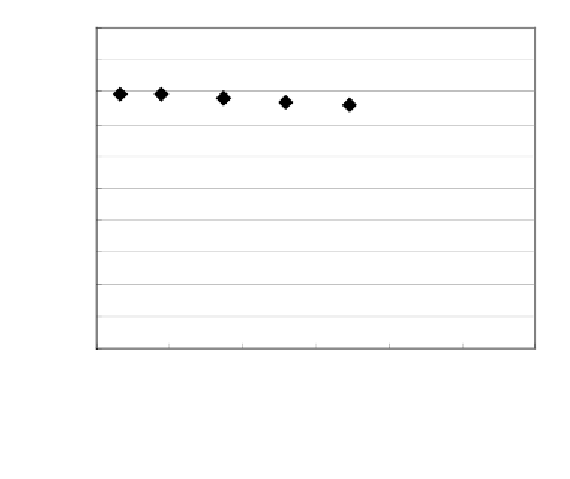
Fig. 4.7 Chemical shift change of 1-
O
-galloylpedunculagin in D
2
O at different
concentrations.
Glc-4
Glc-5
Glc-6
Rhoipteleanin A has a rather unusual structure, in which the two
ellagitannin monomeric units are linked together through a (
S
,
S
)-
flavogallonyl group. The stereoselectivity of the intermolecular
S
-
biphenyl bond formation can be explained on the basis of the
aforementioned hydrophobic association. This ellagitannin was the first
and still unique example of an ellagitannin dimer generated via an
intermolecular oxidative C-C coupling. It is hence quite tempting to