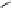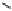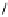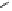Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
later experiments. Meanwhile, similar donor functions of 1-
O
-
acylglucoses have been observed for many other pathways (see
references in Gross, 1999). It thus became evident that the widely
neglected or underestimated phenolic 1-
O
-acylglucose esters, often
previously regarded as metabolically inert compounds or waste products,
occupy a central position in plant secondary metabolism, that is at least
comparable to that of the generally acknowledged role of acyl-CoA
esters.
O
OH
O
+
β
G (
2
)
- Glc
HO
HO
OH
O
OH
HO
G
OH
1
2
G
= Galloyl
G
G
O
O
6
+
β
G (
2
)
- Glc
+
β
G (
2
)
- Glc
O
O
HO
HO
O
O
2
HO
G
HO
G
OH
O
14
15
G
G
O
G
+
β
G (
2
)
- Glc
O
O
HO
4
G
O
O
O
O
G
O
3
O
G
G
O
16
O
G
G
G
3
Fig. 3.5 Enzyme reactions catalyzing the pathway from β-glucogallin (βG,
2
) to
1,2,3,4,6-penta-
O
-galloyl-β-
D
-glucopyranose (
3
) in oak leaves. Positions of newly
introduced galloyl residues are marked by square boxes and numbering of the
corresponding positions on the glucopyranose core.
14
: 1,6-Digalloyl-β-
D
-glucopyranose;
15
: 1,2,6-trigalloyl-β-
D
-glucopyranose;
16
: 1,2,3,6-tetragalloyl-β-
D
-glucopyranose. Glc =
glucose.
Further studies with enzyme preparations from oak or sumac
revealed that the described mechanism,
i.e.
, galloyl transfer from β-
glucogallin (
2
) to glucose hydroxyls, applied to all of the subsequent
transformation reactions up to 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloylpyranose (
3
). As
depicted in Fig. 3.5, it was remarkable to find that these substitution