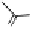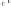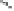Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
2.3 Chemotaxonomic Significance of Oligomeric Ellagitannins
The chemotaxonomic significance of monomeric ellagitannins, which
are widely distributed in dicotyledonous plants, is rather limited, except
for those in certain families. The gluconic acid-based ellagitannins
punigluconin (
18
) and hippophaenin A (
109
) were first isolated in
Punica granatum
(
Punicaceae
) (Tanaka,
et al.
, 1986b) and
Hippophae
rhamnoides
(
Elaeagnaceae
) (Yoshida
et al
., 1991a), respectively.
However, these tannins were later found in several
Lagerstroemia
species in
Lythraceae
(Tanaka
et al
., 1992b) and in many elaeagnaceous
plants. In particular,
Elaeagnus umbellata
produces characteristic dimers
with a gluconic acid-based constituting monomer, such as elaeagnatins B
(
110
), C (
111
), and F (
112
) (Ito
et al
., 1999b).
OH
OH
HO
OH
G =
OH
OH
O
OH
O
O
HO
OH
HO
O
O
HO
A =
OH
COOH
O
O
HO
O
O
O
OH
HOOC
O
(
S
)-HHDP =
O
HO
OH
O
HO
OH
OH
HO
OH
HO
OH
OH
HO
OH
HO
Hippophaenin A (
109
)
HO
OH
HO
OH
HO
OH
HO
OH
R
3
O
OH
O
O
R
4
O
OH
O
O
O
O
O
O
H
O
COOH
O
O
R
2
O
OR
1
O
O
O
O
HO
O
H
O
OH
HO
OH
HO
OH
OH
OH
HO
OH
HO
Elaeagnatin B (
110
): R
1
~R
2
= (
S
)-HHDP, R
3
= R
4
= H
Elaeagnatin C (
111
): R
1
~R
2
= (
S
)-HHDP, R
3
= A, R
4
= H
Elaeagnatin F (
112
): R
1
= G, R
2
= R
3
= H, R
4
= A