Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
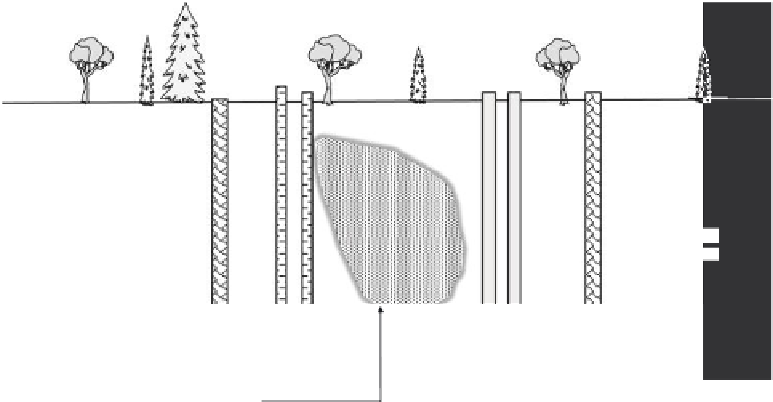
Injection wells for
surfactants and
other additives
Recovery wells for
water treatment
Groundwater
flow direction
Groundwater
flow direction
Monitoring
wells
Monitoring
wells
Contaminant plume
FIGURE 11.3
Schematic diagram of a soil lushing process for removal of contaminants.
In choosing the most appropriate remediation technology, factors to be considered must
include exposure routes, future land use, acceptable risks, regulatory guidelines, level and
type of contaminants, site characteristics, and resultant emissions. Laboratory and ield
treatability tests should be performed to obtain site-speciic information. Soil lushing has
been demonstrated at numerous Superfund sites with costs in the range of $18-50/m
3
for
large easy to small dificult sites (FRTR, 2007). A schematic illustration of the criteria and
tools for evaluating technologies and protocols for environmental management of con-
taminated soils and sediments is shown in Figure 11.1.
A variation of soil lushing is foam injection (Wang and Mulligan, 2004). Foam consists of
tiny bubbles, making an emulsion-like two-phase system where the mass of gas or air cells
is dispersed in a liquid. Surfactants assist in creating and stabilizing the foams. A number of
interesting applications have been investigated regarding its ability to remove various soil
contaminants and is compatibility with pump-and-treat systems and bioremediation. As an
innovative technology, there are various requirements for future development including the
effect of soil matrix characteristics, contaminant speciation, pulsed operation, and surfactant
partitioning on the effectiveness of in situ foam flushing to the subsurface conditions. Site
geological conditions must be investigated and proper selection of the foaming surfactant
and its concentration must be determined. The mechanism of the surfactant actions on the
remediation of contaminated soils is still not clear. Development of predictive mathematical
models will be helpful for optimal surfactant selection for the subsurface.
11.3.5 Soil Washing
Soil washing is applicable for soils contaminated with metals and/or organic contami-
nants (El-Shafey and Canepa, 2003). Soil washing is an ex situ process that uses water to














Search WWH ::

Custom Search