Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
We have shown, from the discussions in the irst part of this chapter and in previous
chapters that our knowledge of the nature of impacts from mechanical- and most hydraulic-
type stressors has resulted in the development of standard practice guidelines and codes
in civil and geotechnical engineering. We have also learned that perhaps the biggest
source of threats to the geoenvironment and its land compartment is the presence of chem-
ical contaminants in the ground. The previous chapters have shown that the various dis-
cards, spills, and loss of materials (chemicals, etc.) and discharge of wastes, either in liquid
form or as solids, are common to all types of human activities that are associated with
(a) households, (b) cities, (c) industries, (d) farms, and (e) mineral and hydrocarbon exploita-
tion. These pose signiicant threats to the land environment and the receiving waters that
are well perceived. Not as well perceived are the threats presented by atmospheric-based
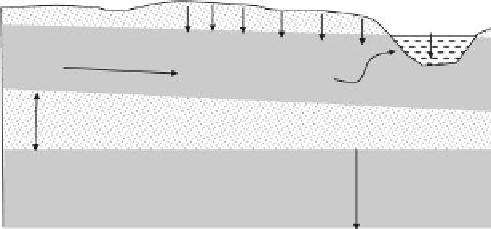
non-point sources such as those shown in illustrative form in Figure 10.21. Under rainfall
conditions, pesticides, herbicides, and other pest control chemical aids have the potential
not only to combine with the rainfall runoff to contaminate the receiving waters, they
also have the potential to iniltrate into the ground and threaten groundwater supplies.
In addition to the non-point sources of contaminants that originate on the land surface
(land-based), there are the non-point sources that originate from precipitation through
the atmosphere containing noxious gas emissions and airborne contaminants (as particu-
lates) from offending smokestacks and other types of smoke discharges. These can be
called atmospheric-based non-point source contaminants. Included in this list are NO
x
Nature and
source of threat
Ground surface
contaminated with
herbicides,
pesticides, etc.
Resources threatened include soil,
river, and unconfined aquifer
Runoff
Infiltration
River
Unconfined aquifer
Aquitard
Confined aquifer
FIGURE 10.21
Demonstration of threats and impacts from atmospheric- and land-based non-point sources. Resources threat-
ened include the river, soil, and unconined aquifer. We presume that the aquitard is suficient to protect con-
tamination of the conined aquifer. If this is incorrect, the conined aquifer will eventually be contaminated by
the water in the unconined aquifer.












































Search WWH ::

Custom Search