Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
including salting, waterlogging, compaction and loss of soil structure, contamination by
pesticides, decreased fertility, and erosion (Gliessman, 1998). Herbicides and pesticides are
(a) persistent in the environment, (b) highly mobile, and (c) can accumulate in the tissues
of animals, producing a variety of ill effects. Data on their concentrations in groundwater
are quite limited. So as not to appear prejudicial, all of these contaminant sources will be
identiied as a group under the term
agro-additives
. These agro-additives ind their way
into the receiving waters and groundwater through surface runoff and through transport
in the ground. Nutrients such as nitrates from animal wastes from poultry or pigs are
other sources of groundwater contaminants (Figure 3.3). Agricultural contaminants are
typically dificult to monitor and estimate due to their dispersion and seepage through
soils into the groundwater.
High levels of nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) from fertilizers, detergents, and
other sources can reach surface waters and lead to eutrophication and excessive algal
growth. Nitrogen, in particular, and, to a lesser degree, phosphorus demand in fertilizers
have grown signiicantly in the last ifty years (USGS, 1998). Eutrophication causes oxy-
gen depletion in the water and production of bad odors, tastes, and colors. Nitrogen, in
particular, originates from fertilizer and manure addition to the soil. Although nitrates
have an important role within the nitrogen cycle, overapplication of manure and fertilizers
impact negatively on plant and microorganism biodiversity. Although ammonium ions
adsorb onto clay particles, nitrate compounds are easily transported. Movement of nitrates
in groundwater depends on aquifer hydraulic conductivity, soil type and moisture, tem-
perature, vegetation, and amount of precipitation. Shallow unconined aquifers have been
Chemical fertilizers,
pesticides, herbicides
Sewage sludge
Manure
Compost
Agricultural soil
Percolation
Runoff
Groundwater
contamination
Surface water
contamination
FIGURE 3.3
Contaminant sources (stressors) for surface and groundwater contamination from agricultural soil. The dashed
line between groundwater and surface water contamination indicates potential contamination of groundwater
from surface water or surface water contamination from groundwater.












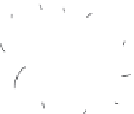












Search WWH ::

Custom Search