Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
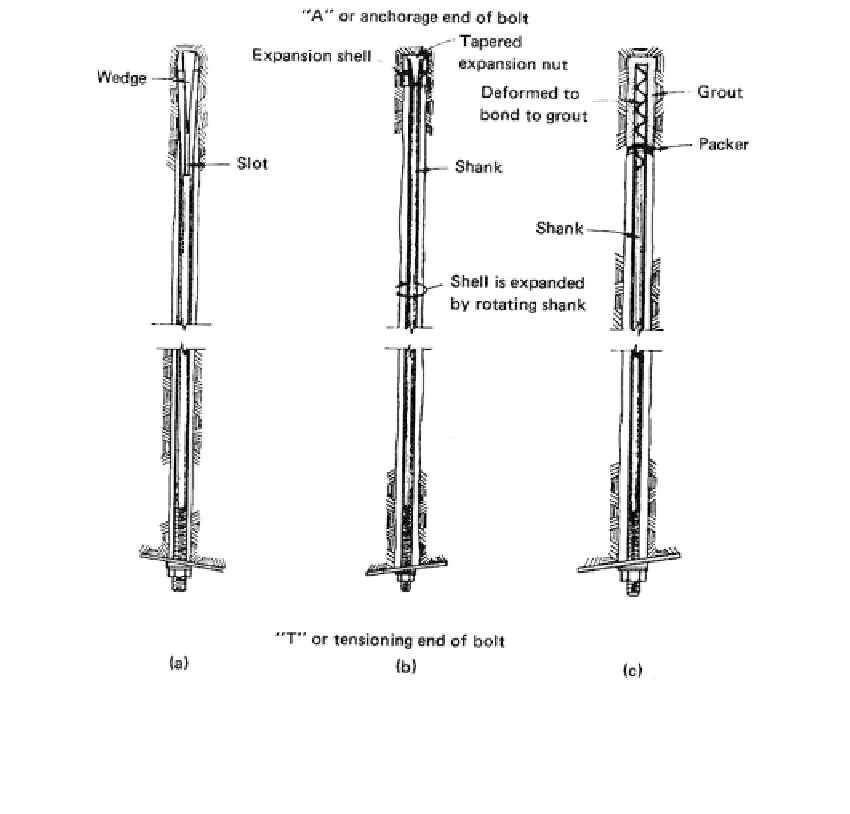
FIGURE 9.118
Types of ordinary rock bolts (anchors): (a) drive-set or slot and wedge bolt; (b) torque-set or expansion bolt; (c)
grouted bolt. (From Lang, T.A.,
Bull. Assoc. Eng. Geol.,
9, 215-239, 1972. With permission.)
Rigid walls
include concrete walls: gravity and semigravity walls, cantilever walls, and
counterfort walls. Anchored concrete curtain walls are considered as semirigid.
Flexible walls
include rock-filled buttresses, gabion walls, crib walls, reinforced earth
walls, and anchored sheet-pile walls.
Soil nailing
is an
in situ
soil reinforcement technique that is finding increasing applica-
tion. Long rods (nails) are installed to retain excavations or stabilize existing slopes. Nails
are driven for temporary installations or drilled and grouted for permanent installations
similar to the procedures described for shotcreting rock masses. Cohesive soils with
LL
20 require careful assessment for creep susceptibility. Soil nailing is dis-
cussed in detail in Elias and Juran (1991).
50 and PI
Wall Characteristics
The general characteristics of retaining walls are summarized in
Table 9.l0.
Also included
are bored piles and root piles, not shown in
Figure 9.125.
Wall Selection and Design Elements
The wall type is tentatively selected on the basis of an evaluation of the cut height, mate-
rials to be supported, wall purpose, and a preliminary economic study.