Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Pollution
infiltration
(3)(2) (1)
River
Pervious materials
Impervious materials
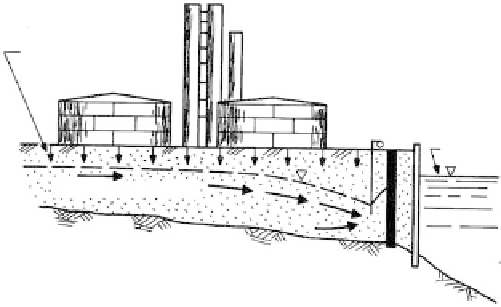
FIGURE 8.60
Pollution control system for chemical plant adjacent to water body. (1) Pollutants would flow through sheet-
pile bulkhead into river. (2) Slurry wall penetrating into impervious strata installed around plant site provides
barrier. (3) Wellpoints periodically remove the effluent that is pumped to storage facilities.
pollutants from plant spills enter the granular materials beneath the plant, mix with
groundwater, and flow through the sheet-pile bulkhead into the adjacent river, unless con-
tained with an impervious barrier and dewatering system as shown.
Solid-Waste Disposal
Disposal in open areas carries with it an inherent potential for the pollution of water
resources, regardless of the manner of disposal or the composition of the waste material.
Industrial wastes subjected to rainfall and groundwater will produce chemical con-
stituents; leachates from open dumps or sanitary landfills usually contain both biological
and chemical constituents.
Since the pollution of an aquifer or nearby water body depends on the ability of the
leachate to seep through the waste and underlying natural materials, waste dumps should
be located over, or in, impervious materials, or the waste dump area should be lined with
impervious materials, or totally confined with a vertical seepage barrier. Location of solid-
waste dumps in old sand and gravel pits or limestone quarries is common and extremely
risky unless dump seepage is contained.
8.5.3
Environmental Planning Aspects Summarized
Water Supply
Evaluate the water quality and water balance quantity, or the withdrawal quan-
tity that does not exceed recharge, as a measure of the permissible withdrawal
for urban populations, farming, and industrial use.
●
Identify the major recharge areas and provide for their protection against block-
age and pollution.
●
Evaluate the potential for land subsidence from overwithdrawal and formulate
contingency plans.
●
Provide contingency plans to supplement water supply for the future when the
normal situation of continuing urban growth and groundwater depletion occurs.
●
Provide for, or plan for, wastewater treatment to maintain and improve water
quality, and provide for solid-waste disposal to avoid or minimize pollution.
●