Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
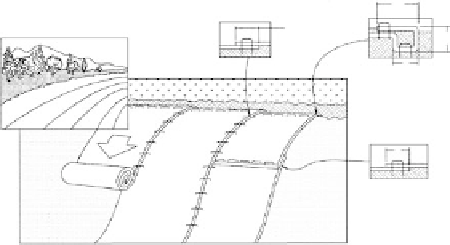
steep slopes a fabric mat or mesh staked to the slope will prevent the seed from washing
away. Biodegradable matting is shown in
Figure 8.11.
Nondegradable meshes are used
where sufficient moisture for rapid growth is lacking. Both degradable and nondegradable
meshes are available for slopes to 45
(1H:1V). Anchored “geocells” have been used on
steep slopes. Another alternative is wattling bundles as illustrated in
Figure 8.12
.
Construction sites
may be treated in a series of procedures as follows:
°
1.
Identify on-site areas where erosion is likely to occur and off-site areas where
sedimentation and erosion will have detrimental effects.
2.
Divert runoff originating from upgrade with ditches to prevent its flow over
work areas. Line large ditches with nonerodible material that will not settle and
crack, permitting ditch erosion to occur. Unlined ditches are suitable in strong
materials where flow velocities will be low. Stepped linings of concrete are used
on steep slopes to decrease water velocities.
3.
Limit the area being graded at any one time and limit the time that the area is
exposed to erosion by planting grass or some other fast-growing native vegeta-
tion as soon as the slope area is prepared.
4.
Retain heavy runoff in large ditches and diminish water velocity with low dikes
of stone or sand bags.
5.
Trap sediment-laden runoff in basins or filter runoff through brush barriers or silt
fences. The latter are made of a filter fabric (Dallaire, 1976).
6.
Carry out postconstruction maintenance to clean ditches, replant bare areas, re-
stake loose wattling bundles, etc.
Installation Summarized
1. Prepare soil before installing blankets,
including applications of lime, fertilizer,
and seed.
2. Begin at top of slope by anchoring
the blanket in 15 cm deep
15 cm wide
trench. Backfill and compact trench after
stapling.
×
3. Roll the blankets (A) down or (B)
horizontally across the slope. Securely
fasten all blankets with staples placed in
spcified patterns.
4. The edges of parallel blankets must
be stapled with 5 to 12.5 cm overlap
depending on blankets type.
5. consecutive blankets spliced down
slope, must be placed end over end with
approximate 7.5 cm overlap. Staple
through overlapped area 30 cm apart.
across entire blanket width.
Biodegradable Net, Typical Specification
1.
2.
3.
C125BN
Material Composition
1.Top Net
Woven, 100% biodegradable,
natural organic fiber
9.3 lb/1000 sq ft (4.5 kg/100 m
2
)
approx wt
2. Coconut Fiber
0.50 lb/yd
2
(0.27 kg/m
2
)
Note:
In loose soil conditions, the use of
staple or stack lengths grater than 15 cm
may be necessary to secure blankets.
Roll Specifications*
Width
6.0 ft (1.83 m)
Length
90.0 ft (27.4 m)
3. Bottom Net
Weight
40lb +10% (18.1 kg)
Woven, 100% biodegradable,
natural organic fiber
9.3 lb/1000 ft
2
(4.5 kg/100m
2
)
approx wt
Thread
Biodegradable
Area
60 yd
2
(50 m
2
)
*All roll specifications are approximate.
FIGURE 8.11
Slope erosion protection with biodegradable matting blankets. (Courtesy of North Amerian Green.)