Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 5.6
Classification of Igneous Rocks
a
Minerals
b
Light-colored rocks
Ortho- clase
feldspar
BHP
With Q
Medium-colored
Dark-colored rocks
Ortho- or Plagio-
clase feldspar
Plagio-
clase
No feld-
spar
Plagioclase
BHP
BHP
HBP
PHOA
OPHBA
Grain size
Without Q
With Q
Without Q
With Q
Without Q
Without Q
No Q
Pegmatite
Granite
Coarse >1 mm
Phanerites
Equigranular
> 1 mm
Grano-
diorite
Monzonite
Tonalite
(quartz
diorite)
Diorite
Gabbro
Peridotite
Pyroxenite
Dunite (0)
Granite
Syenite
Micro-
phanerites
Equigranular
< 1 mm
Aplite
Micro-
syenite
Micro-
grano-
diorite
Micro-
monzomite
Micro-
tonalite
Micro-
diorite
Dolerite
(diabase)
Porphyries
All phanerites are found with phenocrysts (granite porphyry, etc.)
Aphanites
and
aphanite
porphyries
Classes
Trachyte
Quartz,
latite
Felsite (and felsophyre)
Obsidian and pitchstone
Latite
Rhyolite
Dacite
Andesite
Basalt
Scoria
Vesicular
basalt
Pumice
Porous
Note:
Plutonic rocks,
Volcanic rocks,
Border rocks
a
After Pirsson, L.V. and Knopf, A.,
Rocks and Rook Minerals
, Wiley, New York, 1955. Reprinted with permission
of Wiley. (Excludes pyroclastic rocks.)
b
Minerals: A
augite, B
biotite. H
hornblende, P
pyroxene, O
olivine, O
quartz.
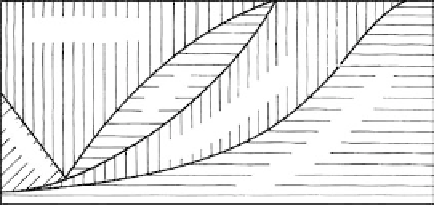
100%
Alkali-feldspar
80%
60%
FIGURE 5.2
Minerals composing the important
igneous rocks. (From Pirsson, L.V.
and Knopf, A.,
Rocks and Rock Minerals,
Wiley, New York, 1955. Reprinted with
permission of Wiley.)
40%
20%
0%
Texture
Intrusives and lavas are grouped as follows:
Phanerocrystalline (phanerites)
have individual grains large enough to be distin-
guished by the unaided eye and are classified by grain size:
Coarse-grained —
●
5 mm diameter (pea size)
Medium-grained — 1 to 5 mm diameter
Fine-grained —
1 mm diameter