Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(e, f)
Adjacent
structure
(a)
(a)
(h)
(k)
Bench mark
(a)
(r)
(k)
(r)
(r)
(k) (r)
(k)
(r)
(r)
Braces
(s)
(g)
(g)
(v)
(L)
(v)
(s)
(L)
(t)
(t)
(v)
(s)
(t)
(v)
(s)
Lowered
water
table
(a)
(v)
Tiebacks
Soils
Rock
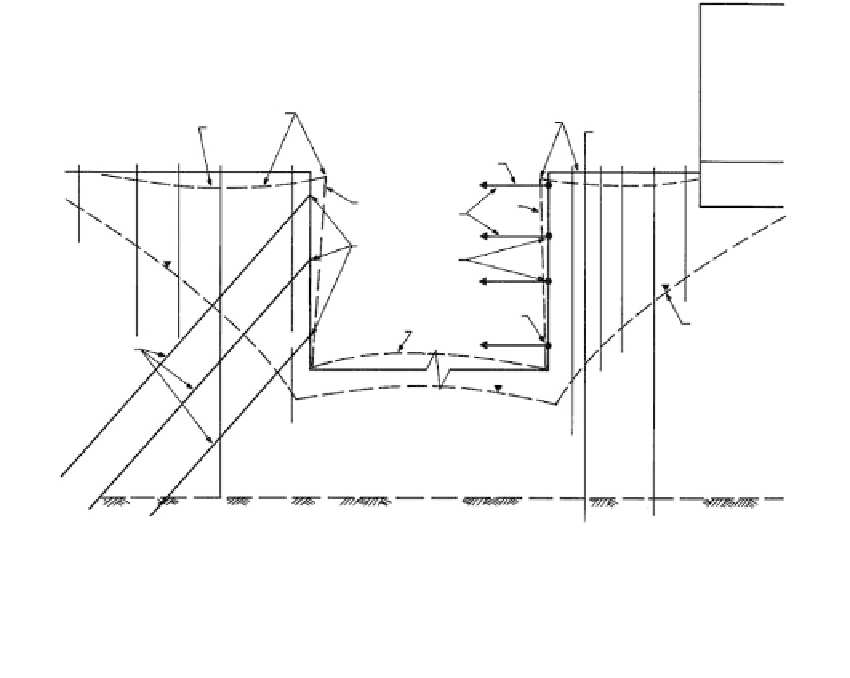
FIGURE 4.37
Instrumentation for excavation retaining structure constructed in soils. Legend: (a) precise leveling; (e)
tiltmeter; (f) pendulum; (L) inclinometer; (g) convergence meter; (k) vertical extensometer; (h) strain meter; (r)
piezometers; (v or w) strain gages; (t) load cells; (s) pressure cells.
from those assumed originally. Most important dam structures, therefore, are instru-
mented and their performance is monitored during construction, during impoundment,
and while in service. Deformations in the foundation and embankment and seepage forces
are monitored.
Instrumentation
Deformations
Most large dams undergo compression under their own weight and are often subjected to
large foundation settlements. Cracks can develop across the core, near the crest soon after
construction, and during reservoir filling. The cracks generally appear near the abutments
as a result of differential settlement along the valley walls, or over irregularities in an
underlying rock surface. As illustrated in
Figure 4.38,
external evidence of deformations is
measured by optical survey (a). Internal evidence is monitored by settlement extensome-
ters or cross-arm devices (k) and strain meters (p). Horizontal strain meters (p) permit the
detection and location of internal cracking when it first occurs.
Pore Pressures and Seepage
Monitoring of pore-water pressures and seepage is necessary in the embankment, abut-
ments, and foundation materials since these phenomena are normally the most critical
factors of dam stability. Critical zones are at the toe, in front of, and below seepage cutoffs
such as core trenches and grout curtains. Piezometers (r) measure pore pressures and the
acoustic emissions device (g) may locate seepage paths and piping zones. Seepage may
often be collected in drainage ditches and measured by weirs.