Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(
A
)
(
B
)
(t)
(a,b)
(a,b)
(r)
Bench
mark
(BM)
(k)
BM
(r)
Bench
mark
(r)
(L)
(k)
Compacted fill
Compacted fill
Compressible soil 1
Weak soils
Compressible soil 2
Strong materials
Strong materials
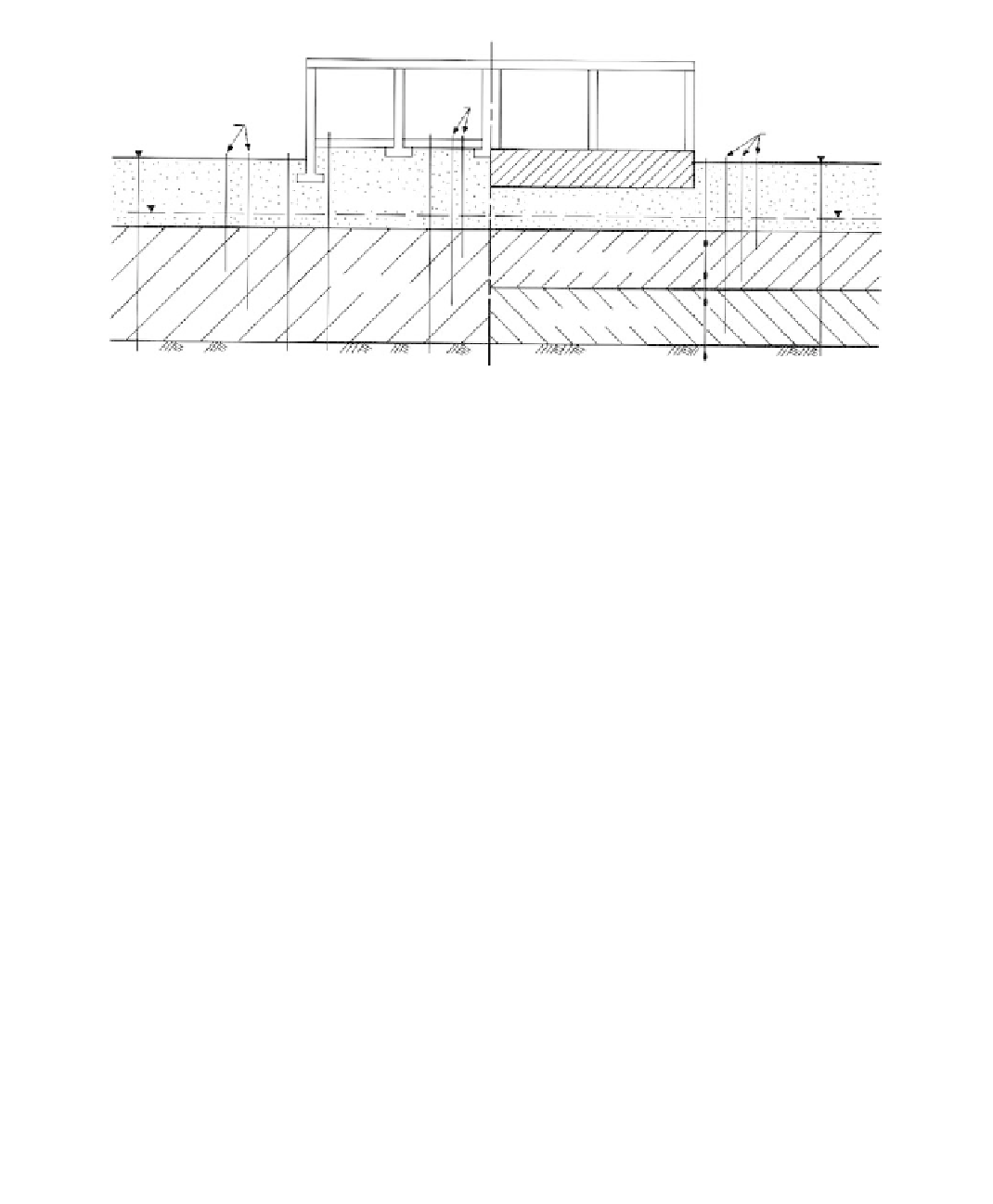
FIGURE 4.34
Instrumentation for building settlements: (A) spread footing-supported light structure; (B) mat-supported
heavy structure. Legend: (a) optical survey; (b) water level device; (k) settlement points; (L) inclinometer;
(r) piezometer; (t) tiltmeter.
Instrumentation
The amounts and time rates of settlement at various locations in the structure and pore
pressures at various depths are monitored with the devices shown in Figure 4.34a. The
inclinometer is installed to measure possible lateral deflections. The data obtained are ana-
lyzed with laboratory test data to determine the magnitude and time rates of the remain-
ing settlement.
Case 2: Structure Undergoing Tilt
Problem
The relatively rigid, mat-supported structure in Figure 4.34b is undergoing tilt from dif-
ferential settlement, which is affecting the balance of turbines.
Objectives
It is desired to determine which strata are contributing to the settlements, to estimate the
magnitude of the remaining settlement, and to judge the time required for its essential
completion in order to arrive at remedial treatments.
Instrumentation
As shown in the figure, building deflections are monitored, as are the compressions occur-
ring in each stratum and the pore pressures.
Case 3: Construction over Soft Ground and Preloading
Problem
An embankment
(Figure 4.35a)
or steel storage tank (Figure 4.35b) is constructed over soft
ground. Preloading is achieved by adding fill or loading the tank with water.