Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
P
= wave pressure
V
= wave velocity
Bumper
P
p
P
b
T
V
p
Transmitter
P
s
V
p
V
s
Acoustic isolator
P
s
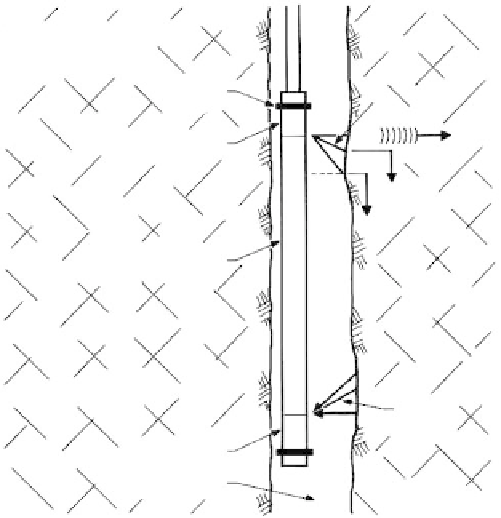
FIGURE 2.57
Schematic of the principles of the
three-dimensional velocity probe. (From
Myung, J.T. and Baltosser, R.W.,
Stability of
Rock Slopes
, ASCE, New York, 1972, pp.
31-56.)
P
p
P
b
R
Receiver
Drilling fluid
(No scale)
transmitter and receiver). For velocity computations, the hole diameter must be known
and is measured with mechanical calipers.
Mechanical calipers
are used to measure hole diameter in rock masses.
●
Recording thermometers
are used to measure fluid temperatures in rock masses.
●
The
electric well logger
is used in soil and rock masses for continuous measure-
ments of resistivity.
●
The
gamma-gamma probe
is used in soil and rock masses to obtain continuous
measurements of
in situ
densities.
●
The
neutron-gamma probe
is used in soil and rock masses to obtain continuous
measurements of
in situ
moisture contents.
●
The
scintillometer
is used to locate shales and clay zones in soil and rock masses.
●
The
rock detector
is an acoustical sounding device used to differentiate boulders
and other obstructions from bedrock. A geophone is set into bedrock and con-
nected to an amplifier, headphone, and oscilloscope. A series of holes is drilled
with a wagon drill, or another drilling machine (
Figure 2.58)
,
while the observer
listens to the volume and nature of the generated sounds.
●
The
Tro-pari surveying instrument
is used to measure borehole inclination and
direction in relatively deep borings in good-quality rock. The instrument works
with a clockwork mechanism that simultaneously locks a plumb device and a
magnetic compass when set in the borehole. The inclination and direction of the
borehole, respectively, are read when the instrument is retrieved at the surface.
●
2.3.7
Groundwater and Seepage Detection
General Groundwater Conditions
Figure 2.59
illustrates various groundwater conditions, which are discussed in detail in
Section 8.3.1
and are summarized as follows:
Static water table or level
(GWL) is located at a depth below which the ground is
●