Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.9
u
value and intersection of
S
at
with
Ω
d
and
D
be the minimum and the maximum distance of
M
0
from
Ω
, respectively
(Fig. 2.10). For a fixed point
M
0
, we have, as
t
and v are varied
⎧
⎨
d
a
,
=
0
,
for
t
<
Effect of initial disturbances
has not propagated to point
M
0
yet,
for
d
D
a
,
u
(
M
0
,
t
)=
=
0
,
a
<
t
<
Effect of initial disturbances has arrived
at point
M
0
,
⎩
D
a
,
=
0
,
for
t
>
Effect of initial disturbances has passed.
For a sufficiently short or long time,
S
at
and
0.
Take initial disturbances as the wave source. The effect of the wave source always
appears on a spherical surface of the sphere of origin
M
0
. Such a type of waves
is thus called a
spherical wave
. Also, the effect of the wave source for point
M
0
will disappear after a sufficiently long time. For example, the propagation of sound
waves has this property.
Take the center of
Ω
have no common part so
u
(
M
,
t
)=
Ω
as the origin
O
. For any specified time instant
t
0
such that
0, consider the region between the spherical surface
S
at
0
−
R
and the sur-
at
0
−
R
>
Fig. 2.10
Minimum and maximum distances of
M
0
from
Ω





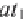

























Search WWH ::

Custom Search