Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
the reflected waves always have opposite phase. Such a phenomenon is called
semi-
wave loss
. The forward, the backward and the reflected waves travel simultaneously
with a common velocity
a
. The effect of reflected waves arrives exactly at the instant
when the effect of forward waves disappears, regardless of the point
x
.
A better understanding of these phenomena can be achieved through drawing the
wave shape at some instant
t
0
for the case
ψ
(
x
)
≡
0 and for some typical wave shape
ϕ
(
x
)
such as triangle wave in Fig. 2.6.
Even Continuation
Find the solution of PDS
⎧
⎨
⎩
a
2
u
xx
,
u
tt
=
0
<
x
<
+
∞
,
0
<
t
,
u
x
(
0
,
t
)=
0
,
(2.70)
u
(
x
,
0
)=
ϕ
(
x
)
,
u
t
(
x
,
0
)=
ψ
(
x
)
.
Solution.
Consider an auxiliary problem
u
tt
a
2
u
xx
=
, −
∞
<
x
<
+
∞
,
0
<
t
,
(2.71)
u
(
x
,
0
)=
Φ
(
x
)
,
u
t
(
x
,
0
)=
Ψ
(
x
)
,
where
Φ
(
x
)
and
Ψ
(
x
)
come from an even prolongation of
ϕ
(
x
)
and
ψ
(
x
)
, respec-
tively,
ϕ
(
x
)
,
x
>
0
,
ψ
(
x
)
,
x
>
0
,
Φ
(
x
)=
Ψ
(
x
)=
ϕ
(
−
x
)
,
x
≤
0
,
ψ
(
−
x
)
,
x
≤
0
.
The solution of PDS (2.71) can be expressed by the D'Alembert formula. It is
straightforward to show that the D'Alembert solution of PDS (2.71) satisfies
Fig. 2.6
Triangle wave





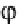




Search WWH ::

Custom Search