Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
sound rays to bend toward the ground, whereas in the upwind direction the rays curve
upward away from the ground. For high-frequency acoustic emissions, this causes greatly
increased attenuation in a
shadow zone
upwind of the source, but little effect downwind.
The attenuation of a low-frequency noise, on the other hand, is reduced by refraction in the
downwind direction, with little effect upwind.
The distance from the noise source to the edge of the shadow zone is related to the
wind speed gradient and the elevation of the source. In a 10- to 15-m/s wind, for a source
height from 40 to 120 m above flat, homogeneous terrain, the horizontal distance from the
source to the shadow zone was calculated to be approximately five times the height of the
source [Shepherd and Hubbard 1985].
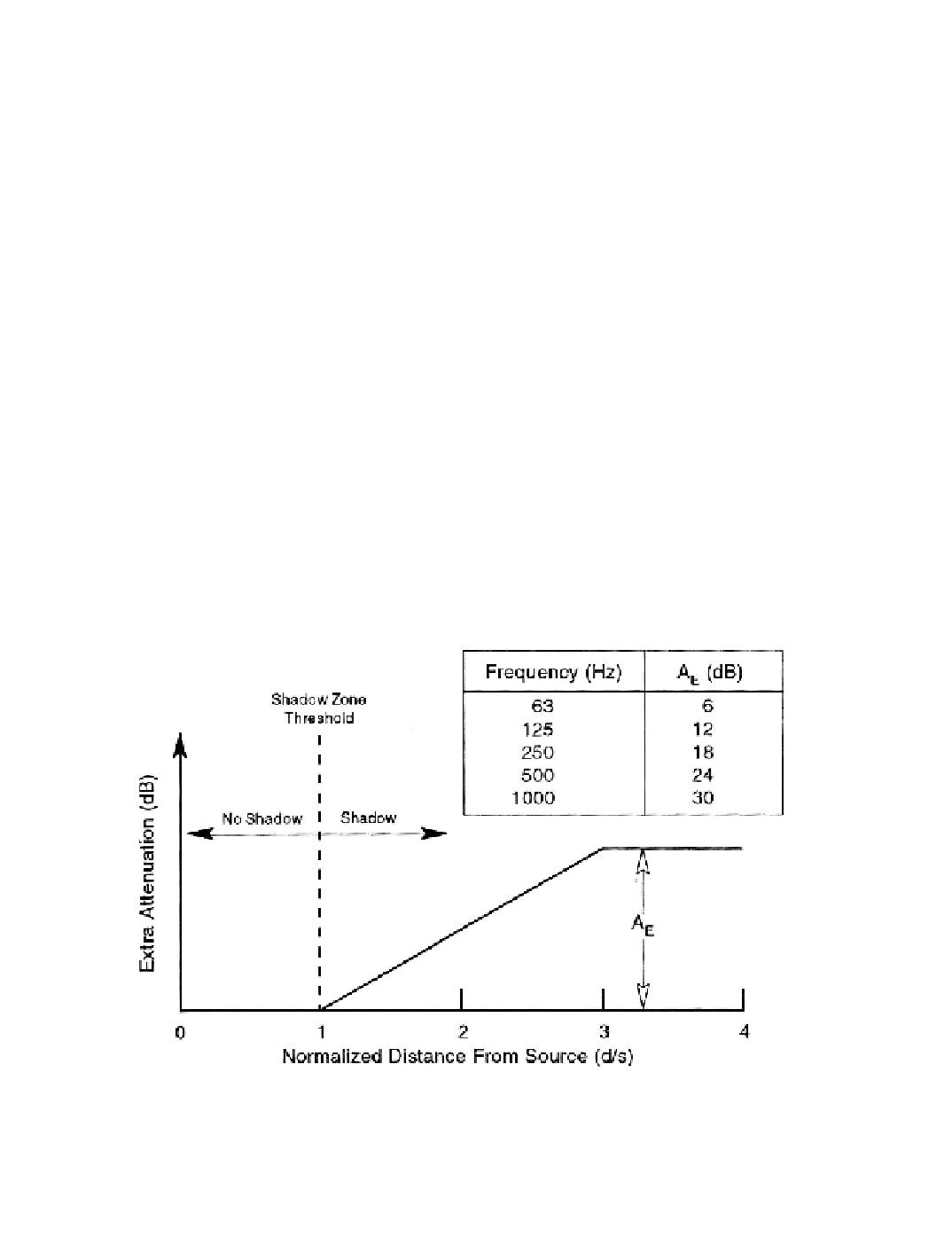
Attenuation exceeding that predicted by spherical spreading and atmospheric absorption
can be found in the shadow zone. This attenuation is frequency-dependent, and the lowest
frequencies are the least attenuated. Figure 7-21 presents an empirical scheme for estimating
attenuation in the shadow zone, based on information in Piercy
et al
. [1977]; SAE [1966];
and Daigle
et al.
[1986]. The estimated extra attenuation is assumed to develop from zero
to a maximum of
A
E
over a distance equal to twice that from the source to the edge of the
shadow zone. The predicted decay in the sound pressure level from the source to the edge of
the shadow zone is caused by atmospheric absorption [ANSI 1978] and spherical spreading.
Within the shadow zone, extra attenuation should be added to these two effects, estimated
according to Figure 7-21.
Note that vertical temperature gradients, which are also effective sound speed gradients,
will normally be present. These will add to or subtract from the effects of wind that are
illustrated in Figure 7-20. Effects of the wind gradient will generally dominate over those
of temperature gradients in the propagation of noise from wind power stations.
Figure 7-21. Empirical model for estimating the extra attenuation of noise in the
shadow zone upwind of an elevated point source.
(s = 5h, 40 £ h £ 120 m, where h =
source elevation) [Shepherd and Hubbard 1985]
Search WWH ::

Custom Search