Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1987]. The following expression for HAWT rotor noise induced by inflow turbulence is
based on the work presented in Grosveld [1985]:
SPL
1/ 3
(
f
) = 10 log
10
[
B
sin
2
q r
2
c
0.7
R
s
2
V
0.7
/
(
d
2
a
0
)] +
K
a
(7-3a)
V
0.7
= 0.7
R
W
(7-3b)
f
peak
=
S
0
V
0.7
/(
H
- 0.7
R
)
(7-4)
where
SPL
1/3
= one-third octave band sound pressure level (dB)
f
= band center frequency (Hz)
q = angle between the hub-to-receiver line and its vertical projection in the rotor
plane (rad)
r = air density (kg/m
3
)
c
0.7
= blade chord at a radius = 0.7
R
(m)
s
2
= mean square of turbulence (m
2
/s
2
)
V
0.7
= blade forward speed at 0.7 radius (m/s)
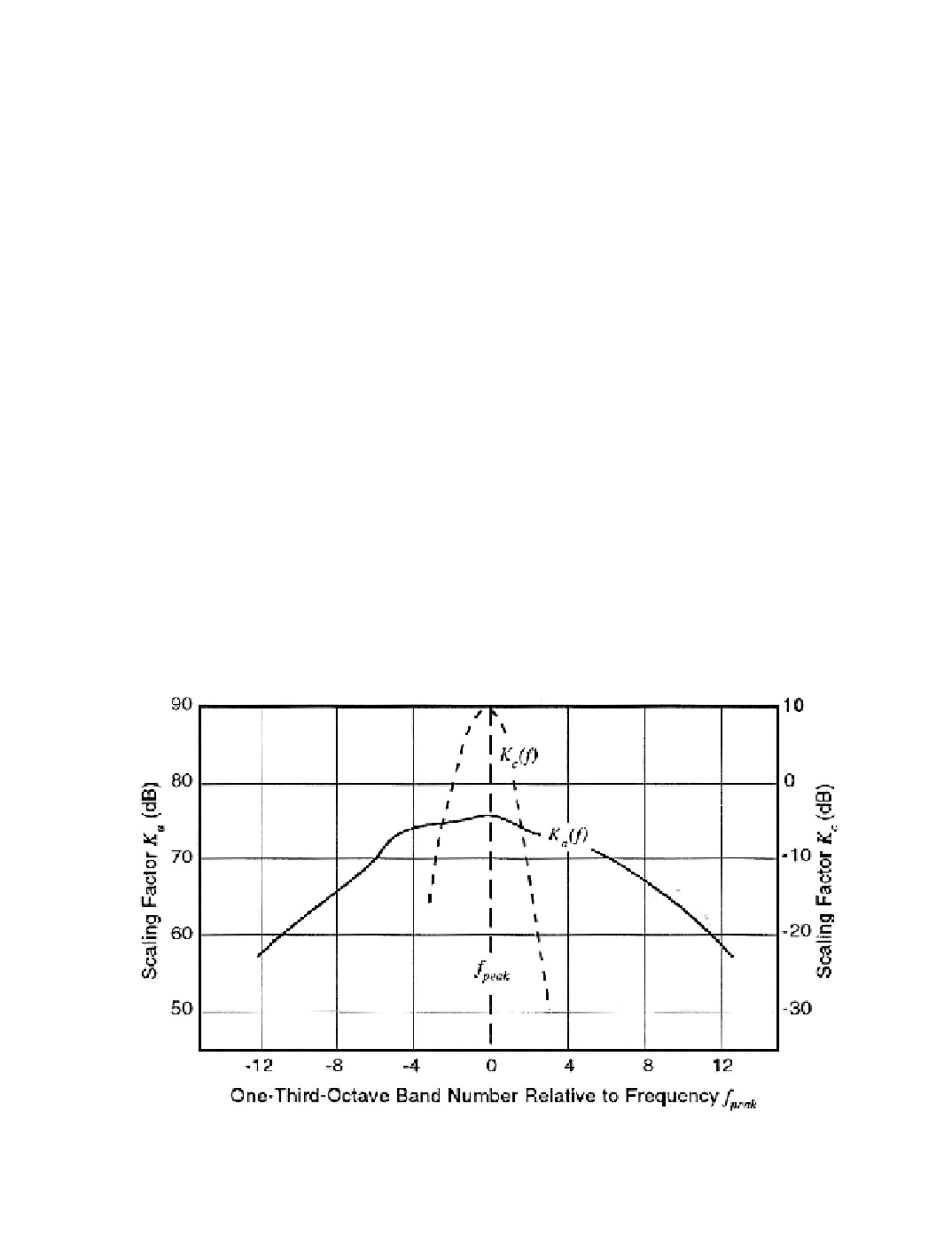
K
a
= frequency-dependent scaling factor (dB; Figure 7-15)
f
peak
= frequency at which
K
a
is maximum (Hz; Figure 7-15)
S
0
= constant Strouhal number = 16.6
H
= hub elevation above ground (m)
A peak in the frequency domain is obtained when
f
=
f
peak
, which corresponds to the
maximum value of
K
a
in Figure 7-15. Inherent in the derivation of Equation (7-3) are the
assumptions that the
turbulence is isotropic
and the
atmosphere is neutrally stable
within
the vertical layer occupied by the rotor. In addition, the noise source is considered to be
a
point dipole
at hub height, and the wavelength of the radiated sound is much shorter
Figure 7-15. Predicted frequency-dependent scaling factors for broadband noise.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search