Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
resolved into their
Fourier components
,
which are pure tones at the blade passage frequency
and integer harmonics of this frequency. These components are evident in the lower-
frequency portion of the downwind-rotor spectrum of Figure 7-5, which shows identifiable
rotational components out to about 30 Hz. The spectrum indicates a peak near 5 Hz and
then a general decrease as the frequency increases [Shepherd and Hubbard 1983].
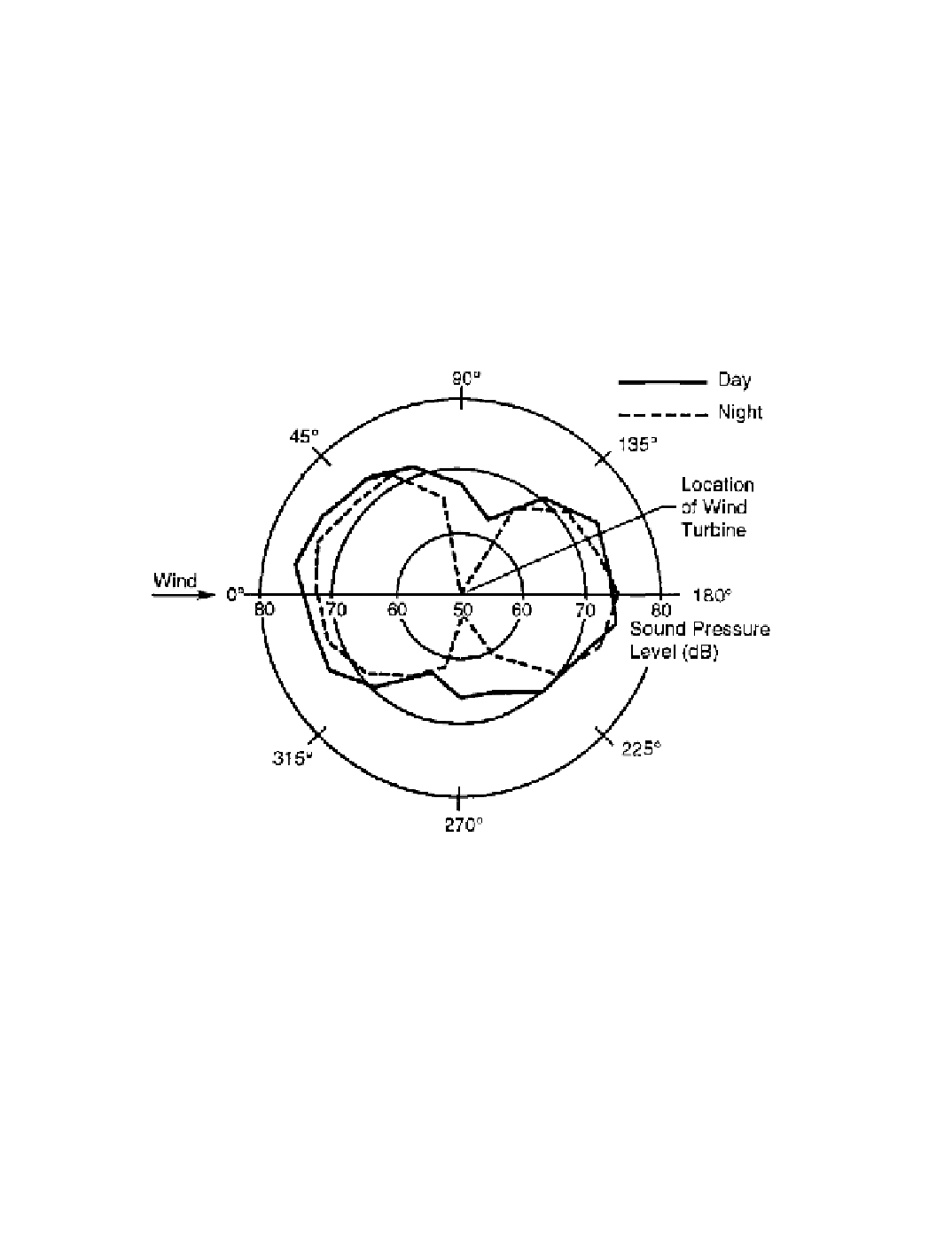
Figure 7-6 illustrates the nature of the noise radiation patterns for low-frequency
rotational noise components. Shown are the results of simultaneous measurements of sound
pressure levels at a frequency of 8 Hz; the measurements were taken at a distance of 200
m around the turbine. Acoustic radiations upwind and downwind are about equal and are
greater than that in the crosswind direction. The two patterns in Figure 7-6 provide a direct
comparison of measurements made at the same nominal wind conditions for daytime and
nighttime operation. The nighttime levels are generally lower than the daytime levels, and
the resulting radiation pattern generally appears as an acoustic dipole. The lower levels are
believed to result from a different atmospheric turbulence structure during the night.
Figure 7-6. Example radiation patterns for low-frequency rotational noise 200 m from
a large-scale HAWT.
(harmonic frequency = 8 Hz, wind speed = 7.2 m/s, power = 100 kW)
[Shepherd, Willshire, and Hubbard 1988]
Kelley, Hemphiil, and McKenna [1982] compare characteristic low-frequency noise
emissions from upwind-rotor HAWTs, downwind-rotor HAWTs, and a VAWT. These
comparisons are based on joint probability distributions of octave-band sound pressure
levels. The authors conclude that a downwind-rotor HAWT presents the highest probability
of emitting coherent low-frequency noise, while an upwind-rotor HAWT appears to have
the lowest probability of emitting such noise. The probability associated with a VAWT
providing coherent noise was found to be between the two HAWT probabilities.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search