Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where
V
e
= effective wind speed (m/s)
V
y
= circumferential (chordwise) wind speed (m/s)
V
n
= wind speed normal to the element (m/s)
Referring to Figure 5-34, the circumferential and normal wind speeds can be calculated from
the free-stream wind speed, the rotor speed, and the axial induction factors as follows:
For
0 £ y £ p :
V
y
=
r
W+
U
1-
a
f
cosy
siny cos
q
(5-51c)
V
n
= -
U
1-
a
f
For
-p £ y £ 0 :
V
y
=
r
W+
U
(1-
a
r
) cosy
V
n
= -
U
(1-
a
r
) siny cos q
(5-51d)
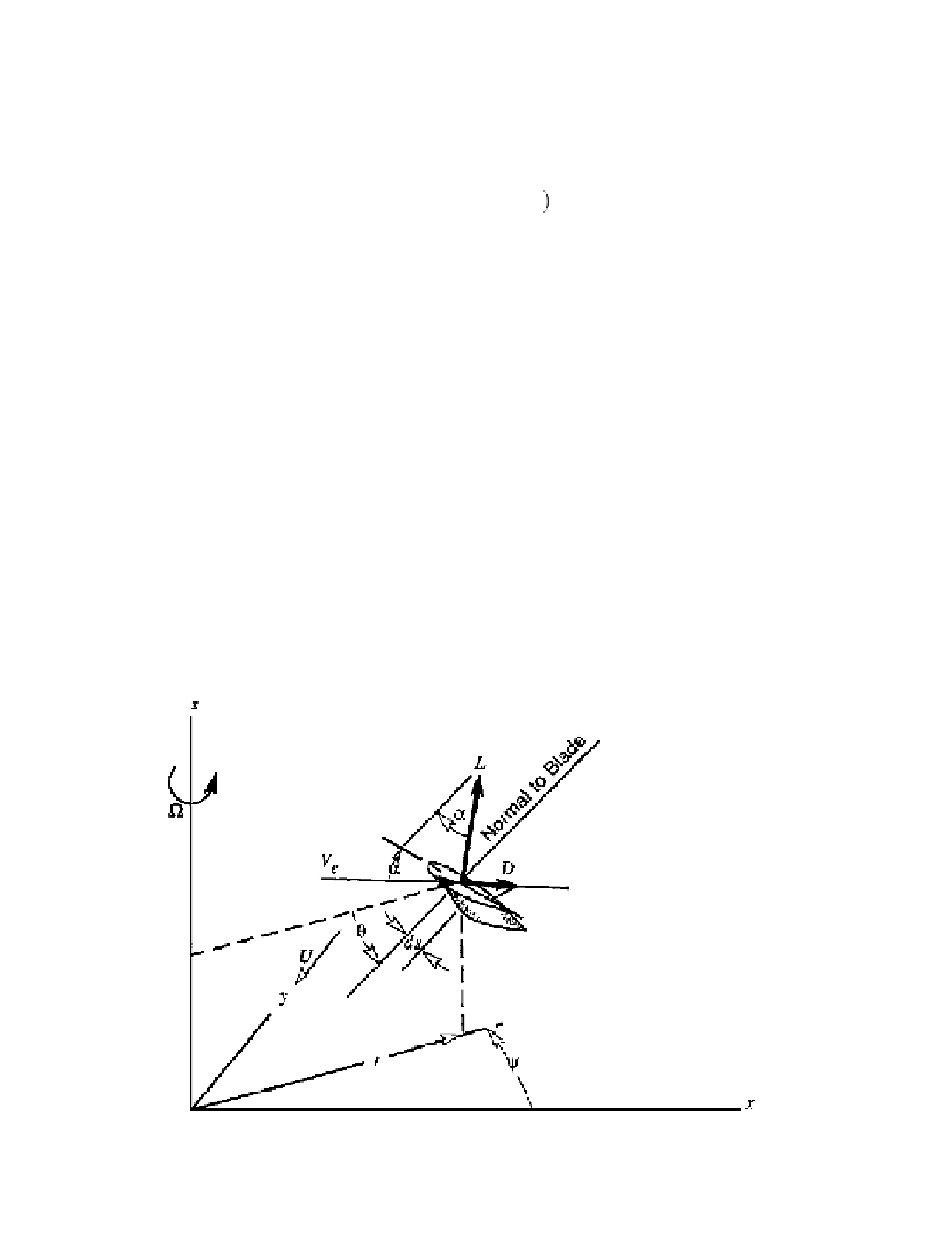
As shown in Figure 5-35, the lift and drag forces on an element of blade of length
ds
produce
a differential torque
dQ
about the axis of rotation that is given by
dQ
=
dQ
KJ
+
dQ
D
(5-52a)
dQ
KJ
= 0.5 r
V
e
cC
L
sin a
cos q
r dz
(5-52b)
dQ
D
= - 0.5 r
V
e
cC
D
cos a
cos q
r dz
(5-52c)
where
dQ
KJ
=
Kutta-Joukowski
(lift) torque contribution (N-m)
dQ
D
= drag torque contribution (N-m)
dz
= incremental height (m)
Figure 5-35. Wind velocity and force diagram for a Darrieus airfoil segment.





Search WWH ::

Custom Search