Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
signiicant inding documented in that comprehensive report is that the measured wind shear
was very low, with monthly power-law exponents in the range of -0.09 to + 0.09.
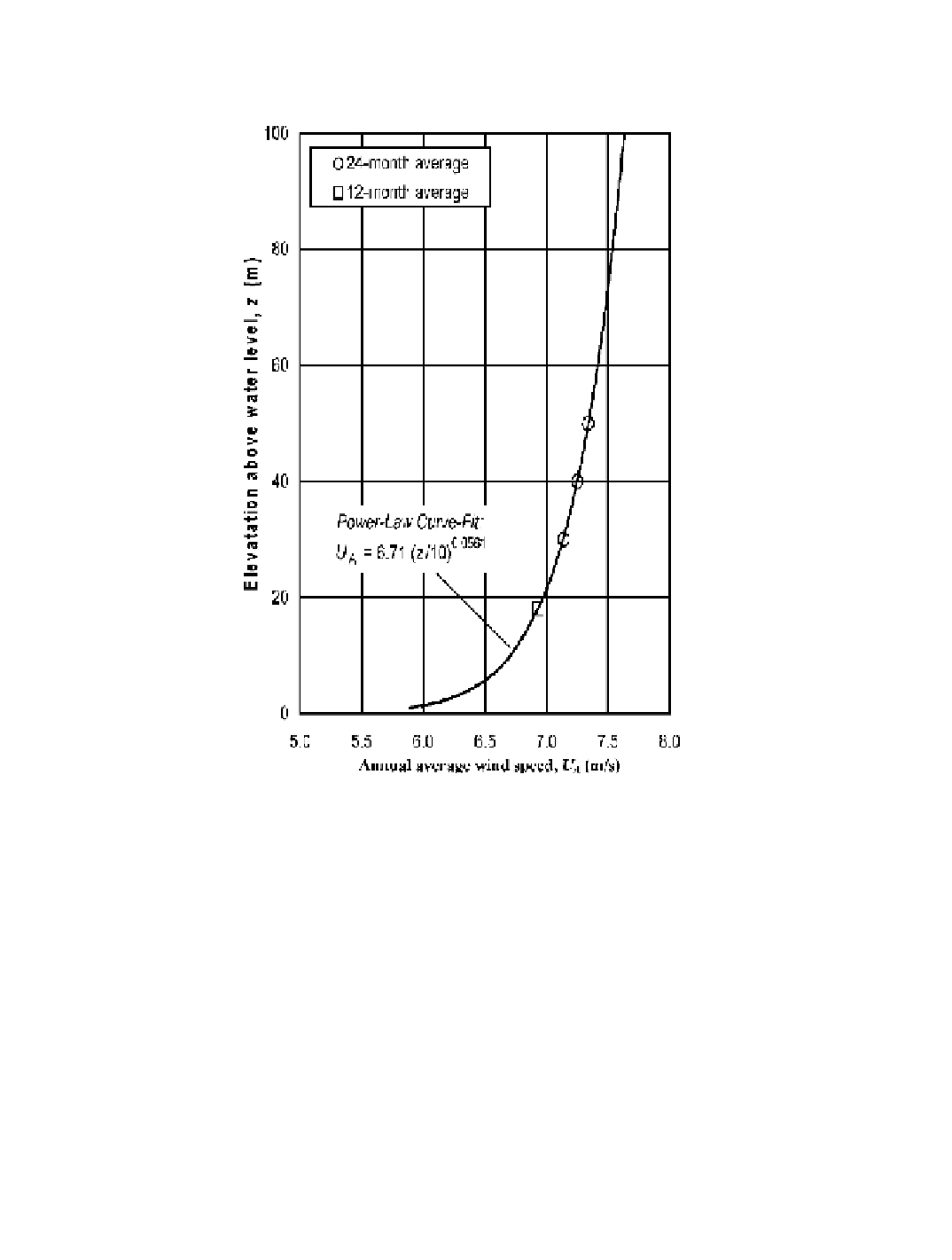
Figure 2-22 shows the vertical proile of the annual average wind speeds measured at the
Cleveland Water Crib monitoring site from October 2005 to September 2007. A power-law
Figure 2-22. Vertical proile of annual average wind speeds measured at the Cleve-
land Water Intake Crib, illustrating the low wind shears characteristic of offshore sites.
[Data: Dykes
et al.
2008].
curve-it of these data points gives a reference annual wind speed,
U
A,R
, of 6.71 m/s and a wind
shear exponent, a, equal to 0.0561. The following equations and Figure 8-13 can now be used
to calculate a surface roughness length for this site [Spera and Richards 1979]:
/
(2-27a)
a = a
[1 - 0.55 log(
U
R
)]
0
5
a
0
z
0
=
10
(2-27b)
where
a
0
= wind shear power law exponent at 1 m/s reference wind speed
z
0
= empirical surface roughness length (m)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search