Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
addition, they are research products and means for communication. In the follow-
ing, some of these model purposes and potentials are elucidated.
Models Can Help to Analyse the Results of Empirical
Investigations or a Theoretical Problem that Is Not
Accessible Through Statistical Data Interpretation Alone
Models can generally work within two types of situations - helping to solve
empirical problems where a model needs to meet certain requirements resulting
from field or laboratory measurements (data), and for theoretical purposes that
investigate conditions and possibilities based on assumptions. Models usually go
beyond situations and questions that require only data interpretation and statistical
analysis. A good example for such a modelling approach is the complex competi-
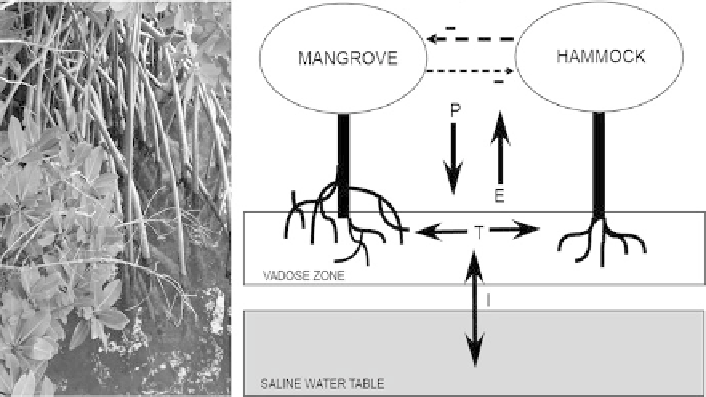
tion situation between hardwood hammocks and mangroves (see Fig.
2.2
). In the
marshlands of South Florida Everglades (U.S.) hardwood hammocks and man-
groves occur with distinct boundaries between their respective areas. Teh et al.
(2008) applied a spatially-explicit simulation model to examine the effects of the
salinity of the aerated zone of soil overlying a saline body of water, known as the
vadose layer, as a function of precipitation, evaporation and plant water uptake
(Fig.
2.2
right) on the vegetation. The model predicted that mixtures of saline and
freshwater vegetative species represent unstable states, which are highly dependent
on initial conditions of the system. The model conceptually explains the mechanism
Fig. 2.2 Model on separation of mangroves (
left
) and hardwood hammocks in the marshlands of
South Florida Everglades (U.S.). The model focuses on water transport and effects of the salinity
on the vegetation (
P
precipitation,
E
evaporation,
T
transpiration,
I
infiltration, Teh et al. 2008)