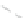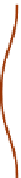Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ρ
age group
1-
5
corrected
tree height i
ρ
total
Ymin tree i
α
seg
0
corrected
crown base i
horizontal distance
crown base 0
crown base i
Δ
tree base
Tree i
Tree 0
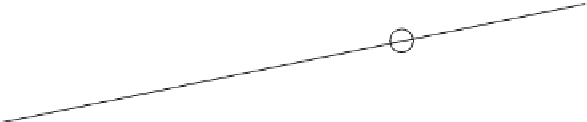
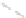
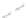
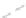
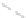
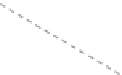
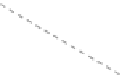
Fig. 11.6 Shadowing segments (
dark
) of a neighboring tree
i
within a light cone above the base
point z of segment
seg
0
(adapted from Lanwert 2007)
X
n
R
2
Tree
ð
i
Þ
cf
TreeðiÞ
M
ð
seg
i
Þ
TM
TreeðiÞ
B
ð
seg
0
Þ¼
with
c
i
¼
(11.1)
!
;
!
Þ
2
Dist
ð
segbase
0
segbase
i
þ
c
i
i¼
1
seg
i
2ConeðaÞ
and with
M
(
seg
i
) representing the needle biomass of shadowing segment
i
and
Dist
(
segbase
0
!
) giving the distance between the two segment base points.
TM
Tree
(
i
)
is the light transmission coefficient of the tree to which the segment object
seg
i
belongs. The quotient
R
2
/cf
represents a correction factor taking into account
the distribution of the needle mass over the crown radius
R
of the tree the segment
seg
i
belongs to.
The following code sample (taken fromLanwert 2007, adapted) shows a “for”-loop
which is executed in a rule applied to an arbitrary segment s and which makes use of a
query, enclosed by (*
!
,
segbase
i
*) and defining a set of subgraphs, using a search pattern and
four conditions. The search pattern looks for all segments (named a) connected by a
daughter relation (directly or indirectly) with a tree element (named b). The first two
conditions exclude all matches where the tree element (b) is equal to the parent tree
element of themain segment s andwhere the top segment of b is outside the cone. Thus
most trees in far distance are eliminated. The second two conditions exclude all
...