Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
benefit of simultaneous multielement analysis. The detection limits are much lower
than ICP-OES at or below the ppb range. Additionally, ICP-MS can provide isotopic
information as described earlier.
Numerous ICP-MS methods have become available from research commu-
nities, the U.S. EPA, and other organizations. An example of development from
recent studies includes the use of ICP-MS or IC-ICP-MS for the speciation
analysis of several environmentally important elements such as Cr, As, and Se.
Several regulatory methods based on ICP-MS have been promulgated by the U.S.
EPA. These include Method 200.8 for the analysis of water, wastewater, and
wastes. Other U.S. EPA water methods using ICP-MS include Methods 1683 and
1640. ICP-MS based method in SW-846 is Method 6020 for solid wastes, which
has been approved for RCRA program since 1995. The latest CLP SOW
incorporates ICP-MS instead of GFAA. Besides these U.S. EPA methods, other
consensus methods have become available from several agencies such as ASTM,
APHA, and DOE.
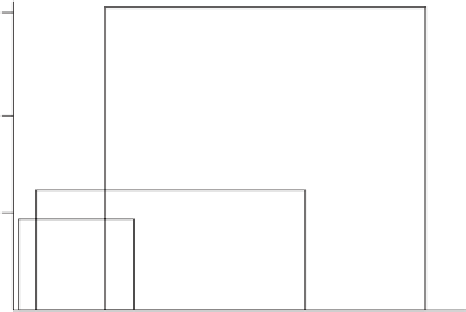
GC-MS and LC-MS Applications: General applications of GC-MS and LC-MS
techniques can be illustrated in Figure 12.9 with regard to molecular weight
and compound's polarity. As shown, GC-MS can be used to analyze a small
percentage of total compounds (approximately 9 million registered), because GC
imparts little or no heat to analyte molecules. A fortunate aspect of GC-MS is that
most pollutants of environmental importance have molecular weight less than
approximately 500, and some of the low-volatility compounds can be made
amenable to GC-MS by derivatization (Chapter 7). Complementary to GC-MS,
LC-MS can virtually analyze all semivolatile, nonvolatile, thermally labile, or
charged molecules. An added advantage of LC-MS is that it allows direct injection
of ''aqueous'' samples and eliminates the need for time-consuming sample
preparation and sometimes chemical modifications.
100,000
APEI
10,000
APCI
1000
GC/MS
Nonpolar
Very polar
Analyte polarity
Figure 12.9
Applications of GC-MS and two major LC-MS techniques (
#
Agilent Technologies,
Inc., 2001, Reproduced with permission, Courtesy of Agilent Technologies Inc.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search