Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
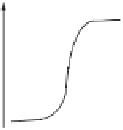
A typical plot of E vs. V has a characteristic sigmoid (S-shaped) curve. The part of
curve that has the maximum change marks the equivalent point of titration. This
point can also be determined by the slope of the curve (i.e., the first derivative,
E
=
V) vs. V plot (Fig. 11.4).
Figure 11.4
A potentiometric titration
curve: (a) E vs. V plot and (2) The first
derivative plot of
V
E
V
E
V
(mL)
V
(mL)
E=V vs. V
Potentiometric titrations can be used for not only redox reaction but also acid-
base, precipitation, and complexation. Examples of acid-base titration include
acidity and alkalinity in water quality measurement (Section 6.3.3). The classical
volumetric titration methods are based on the chemical color indicators for the
determination of end point. The advantage of potentiometric titration for the
measurement of acidity and alkalinity is the automated nature of the procedure.
Since the end point is based on the millivolts (mV) of the solution, another added
advantage is that the titration is not subjected to interference from colored
samples.
11.3 VOLTAMMETRIC APPLICATIONS
IN ENVIRONMENTAL ANALYSIS
The use of voltammetric techniques, although important within analytical chemistry,
is not as widespread as it could be. In environmental labs, the most important
applications include dissolved oxygen (DO), chlorine, and metal species analysis.
DO can be measured by either galvanic cells or polarographic (electrolytic) cells.
Free and residual chlorines are important in monitoring of drinking water quality.
Their analyses by volumetric titration have been described in Section 6.3.6. We
introduce here the automated amperometric titration technique. Finally, we briefly
introduce metal analysis by anodic stripping techniques.
11.3.1 Measurement of Dissolved Oxygen
There are two types of DO measuring probes. If the electrode materials are selected
so that the difference in potential is 0
5 V or greater between the cathode and
anode, an external potential is not required and the system is called galvanic. The
DO probe of this type is usually Ag or Pb with KOH as the electrolyte. If an external
voltage is applied, the system is called polarographic. The polarographic probe has a
:









Search WWH ::

Custom Search