Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
After
Before
Column bleeding
Noise
Spike
Wander/drift
(b)
Clean
blank
run
Fronting
Tailing
Ghost
Split
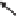
Figure 10.12
Example chromatographic problems used in troubleshooting; (a) Baseline problems
and (b) Peak problems
different,
it will be noted whether
it
is for GC or HPLC. Some of
the
chromatographic problems illustrated below are shown in Figure 10.12.
Baseline Problems In GC, the common causes for a noisy baseline could be
contaminated gases, inlet, column and/or detector, septum degradation, or leaks
when using an MS, ECD, or TCD detectors. When erratic baseline (wander and
drift) appears, it is a sign of contaminated gas and column, incompletely conditioned
column, change in gas flow rate, or large leaks at septum during injection and for a
short time thereafter. When a rise in baseline occurs as a column approaches high
temperature, this is typical of column bleeding when the maximum allowable
column temperature is approached or exceeded. Here ''bleeding'' refers to the
breakdown of GC column stationary phase at a high temperature. The column needs
to be re-conditioned, trimmed, or replaced. In HPLC, a noisy baseline commonly
occurs with a dirty sample, dirty detector cell, trapped air bubbles, or not fully
equilibrated mobile phase. Drifting baseline is a sign of not-fully equilibrated
system, change in mobile phase because of continuous sparging, or change in
temperature.
Peak Problems These include fronting peaks (likely caused by sample
overloading), tailing peaks (such as caused by severe column contamination),
ghost peaks (caused by contaminated sample or mobile phase, carry-over from a
previous injection, inlet, septum bleed), split peaks (bad injection technique), and
changes in peak size (caused by change in detector response, split ratio, or injection
volume, etc.).
Retention Time Problems Retention time is not unique to an analyte but
should not be changed at a given analytical condition. In GC, changes in column
temperature and carrier gas velocity or leaks (in septum,
injector or column

Search WWH ::

Custom Search