Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
of the column effluent takes place. Consequently, the detector undergoes a marked
rise in temperature. Because of the nature of the detector response, TCD is relatively
a universal detector but with low sensitivity. Hence, its use in environmental analysis
is limited except for the measurement of major constituents of air. They have
remained as a popular GC detector, particularly for packed columns and inorganic
gas analysis such as H
2
O, CO, CO
2
, and H
2
.
Flame Ionization Detector
As the name implies, the FID uses H
2
-air flame to burn organic compounds that
undergo a series of ionization reactions. Reactions involved in the H
2
-air flame
include thermal fragmentation, chemi-ionization, ion molecule, and free radical
reactions. However, the exact reaction mechanisms are not well understood. The
amount of ions produced is roughly proportional to the number of reduced carbon
atoms present in the flame, and hence the number of molecules. Because the flame
ionization detector responds to the number of carbon atoms entering the detector per
unit of time, it is a mass-sensitive, rather than a concentration-sensitive device. As a
consequence, this detector has the advantage that changes in flow rate of the mobile
phase have little effects on detector response.
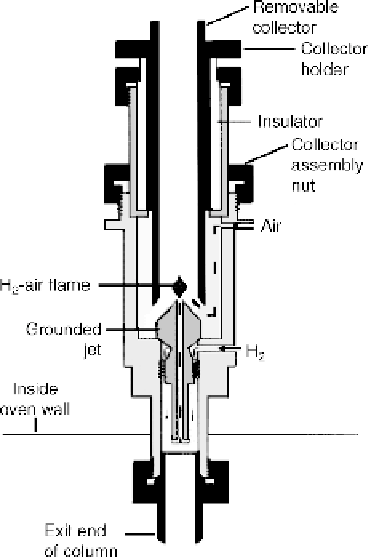
As shown in Figure 10.8, the sample effluent from the column is mixed with H
2
and air and then ignited electrically at a small metal jet. There is an electrode
Figure 10.8
Flame Ionization Detector
(FID) (
Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2006,
Reproduced with permission, courtesy of
Agilent Technologies, Inc.)
#
Search WWH ::

Custom Search