Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Sample
M
+
A
-
Eluent
Eluent
H
+
Cl
-
Na
+
OH
-
Analytical
column
M
+
A
-
Na
+
OH
-
M
+
A
-
Na
+
A
-
HCl
NaOH
Suppressor
column
Figure 10.6
Principles of ion
chromatography for anion analysis (left)
and for cation analysis (right). Only
monovalent anion (A
) and monovalent
cation (M
þ
) are illustrated
M
+
OH
-
H
2
O
H
+
A
-
H
2
O
Anion analysis
Cation analysis
During anion analysis, anions are impeded by the attraction ofNR
3þ
groups
bound to the resin in the analytical column. These anions are separated into discrete
bands on the basis of their affinity for the exchange sites of the resin.
Sodium carbonate (Na
2
CO
3
) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO
3
) are commonly
used as the eluents, and when they are used, the following reactions take place in the
suppressor column:
2RSO
3
HþNa
2
CO
3
!
2RSO
3
NaþH
2
CO
3
ð10
:
9Þ
RSO
3
HþNaHCO
3
!
RSO
3
NaþH
2
CO
3
ð10
:
10Þ
The cations (Na
þ
and others) are retained in the suppressor column and the
separated anions in their acid form are measured using an electrical-conductivity
cell. The output of an IC system is a plot of conductance vs. time. It should be noted
that the suppressor column will eventually become depleted and will have to be
regenerated. Regeneration is accomplished using HCl for the cation exchange (anion
analysis) or NaOH for the anion exchange (cation analysis) (Fig. 10.6).
10.2.4 Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
SFC is a hybrid of gas chromatography and liquid chromatography that combines
some of the best features of each. In Chapter 7 (Sec. 7.3.7), we discussed
how supercritical fluid of CO
2
is formed and its use to better extract certain organics.
In SFC, the supercritical fluid form of CO
2
is used as a carrier fluid in the separation
column just as other mobile phases used in GC or HPLC. Supercritical fluid
has some preferred physicochemical properties; some are analogous to gas and some





























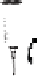








Search WWH ::

Custom Search