Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
RE400 (type A)
Snyder
column
Control box
Vaccum pipe
Cooling water
pipe
Cock
Volume knob
Opening to pour
sample
Motor
Flask remover
Flask clamp
Cooling tube (type A)
Erlenmeyer
flask
Flask clamp
Distilling flask
Receiver flask
Steam duct holder
Collection
tube
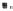
BM400
Stand
(a)
(b)
Water bath BM400
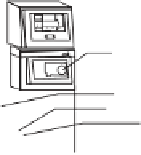
Figure 6.2
Apparatus used to concentrate: (a) Kuderna-Danish (K-D) evaporative concentrator
(Courtesy of Kontes Glass Company), and (b) Rotary evaporator (rotavap) (Courtesy of Yamato
Scientific Co., Ltd, Japan)
removed under vacuum (with a simple water aspirator or a vacuum pump), trapped
by a condenser, and is collected in the receiver flask. If samples contain very volatile
solvent such as diethyl ether or methylene chloride, some solvents in the receiver
flask may be evaporated and lost by vacuum. To prevent this, a cooling bath on the
receiver or dry ice condenser can be used.
Digestion
Digestion is commonly used for metals, total phosphorus, and total nitrogen under
heated conditions. The digestion procedure breaks down an organically bound
substance and converts the substance to the analyzed form by using liquid oxidizing
agents such as H
2
SO
4
,HNO
3
, HClO
4
, HCl, or using oxidizing mixtures such as aqua
regia. Sometimes, addition of bromine (Br
2
)orH
2
O
2
to mineral acids will increase
their solvent action and hastens the oxidation of organic materials in the sample. If
the decomposition of silicates is needed, HF is used, but never use glass containers
with HF. Digestion is sometimes dangerous, particularly if the sample contains a
high amount of organic compounds. Always wear goggles, lab coat, and use heavy-
duty gloves in case of acid spills during acid digestions.
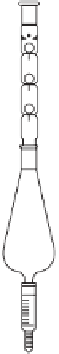
Extraction
Chemicals have different solubilities in different solvents, which can be used to
selectively remove a solute from a mixture. This extraction process is often used as a
sample preparation to concentrate trace organic compounds. Two classical
extraction procedures are the liquid-liquid (L-L) extraction using a separatory
funnel for liquid samples, and Soxhlet extraction for solid samples (soil, sludge).









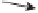












Search WWH ::

Custom Search