Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
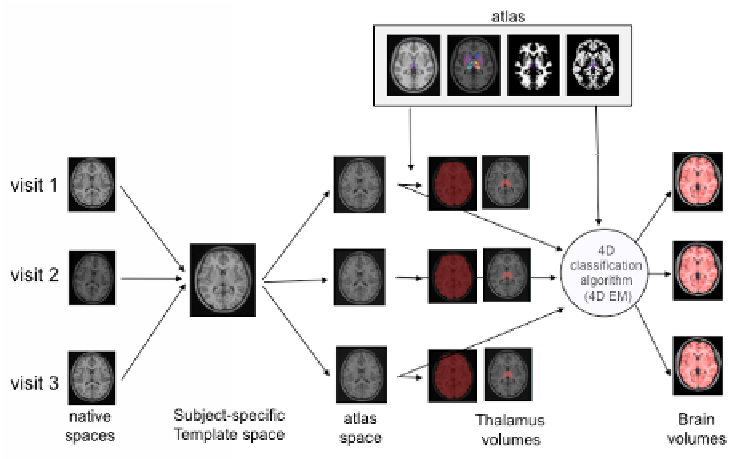
Native T1w images of e
formation from native spa
subject-specific template sp
non-local patch-based segm
T1w images re-sampled in
brary of priors [13]. A 4D
GM and WM volumes (the
the WM volumes). The tot
WM volumes.
As T1w images of each
specific template that was n
left and right thalamus def
each time point's T1-weig
right and left volumes were
All data from the three g
to the same processing step
volume calculation. For eac
computed and thalamus vol
ach visit were re-sampled once via the concatenated tra
ace to the subject-specific template space, and from
pace to the ICBM152 template space. A multi-resoluti
mentation technique was used to extract the brain from
nto the ICBM152 template space, using BEaST with a
EM classification algorithm [14] was used to segment
e lesions were masked for the classification and added
tal brain volume is computed as the sum of the GM
ans-
the
ion,
the
a li-
the
d to
and
h time point were also registered to a non-linear subje
non-linearly registered to the population template [12],
fined on the ICBM152 template were warped back o
ghted images using the concatenated transformations. T
e combined for analysis.
groups (patients, NC, and NIHPD groups) were submit
ps defined above: pre-processing, spatial normalization,
ch visit of each subject, brain and thalamus volumes w
lumes were normalized by the brain volumes.
ect-
the
onto
The
tted
and
were
Fig. 1.
Longitudinal pipeline
with a subject with 3 visits
used to compute the brain and the thalamus volumes. Examp
mples
Longitudinal Mean and In
We wanted to model the ind
growth rate at the time of th
the tangent line at the time
of the growth curve at that t
ndividual Trajectory Models
dividual growth curves in order to estimate the volume
he first attack. The growth rate was defined as the slope
of the first attack and was found using the first derivat
time.
and
e of
tive
Search WWH ::

Custom Search