Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
0
Density-Dependent
-1
-2
-3
-4
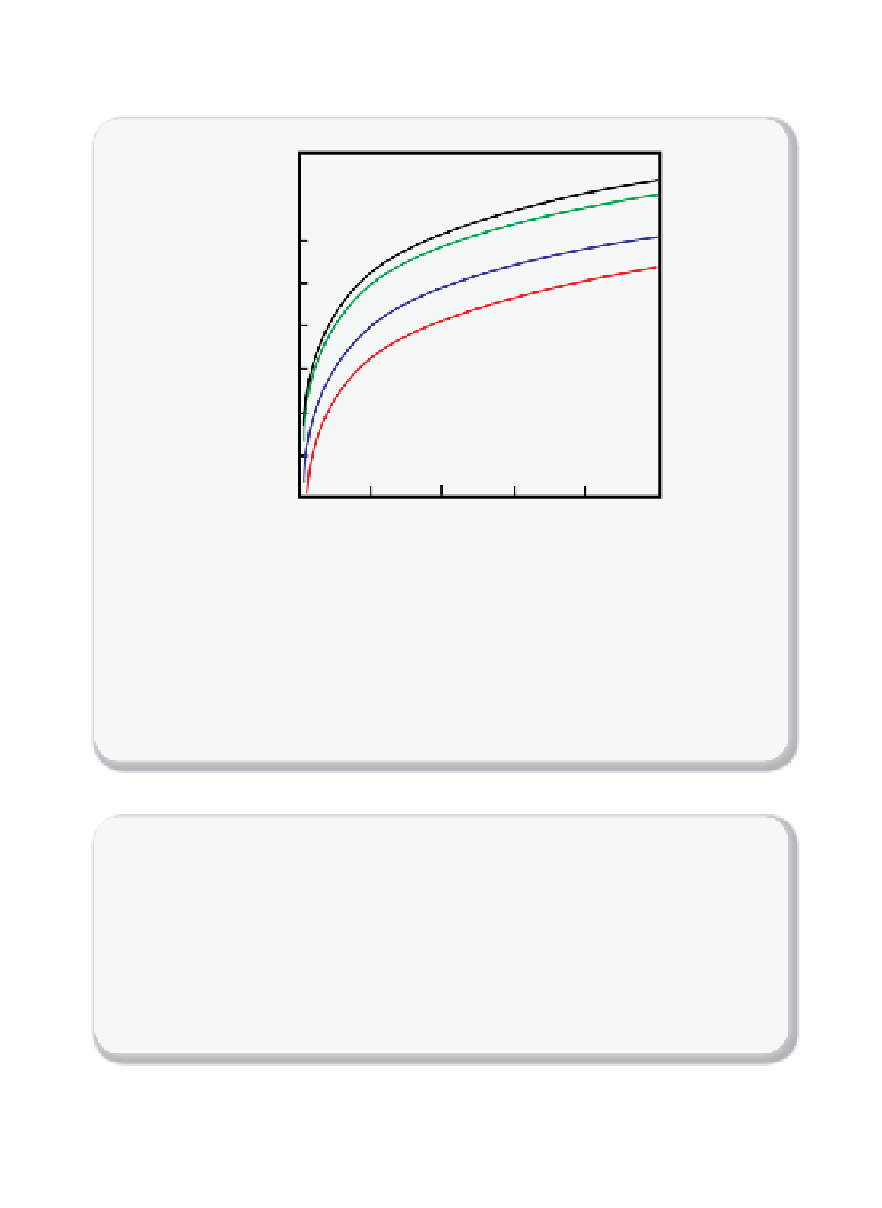
L=500 m
L=100 m
L=10 m
L=5 m
Passive
-5
-6
Approximate Net Ecosystem Exchange (NEE) (4.4 ×10
-7
kg m
-3
s
-1
)
-7
-8
0 2 4 6 8 10
Wind Velocity (m/s)
Figure 10.4.8
Active versus passive fl ows
Delineation of active (density-dependent) vs. passive (not density-dependent) fl ows as
controlled by seepage fl ux and wind speed for various different scales of surface CO
2
seepage. The fi gure shows that large seepage fl uxes (10
4
times that of natural plant CO
2
uptake) will produce density-dependent fl ows even for relatively high wind speed (e.g.,
8 m/s) for seepage over 100 m length scales.
Figure adapted from Oldenburg and Unger
[10.43]
.
Question 10.4.1 Comparative environmental risks
Consider the HSE risks of current energy-related technologies as made obvious
by recent failures such as the Deepwater Horizon drilling platform fi re and
Macondo Well blowout, the Big Branch coal mine fi re, and the San Bruno, CA,
natural gas pipeline explosion. How would potential failures of sequestration
system components (pipelines, geological storage sites) compare with existing
energy-related technology failures? Compare and contrast by considering
effects such as fl ammability and explosion potential, proximity of population, etc.
importantly relative to doing nothing about greenhouse gas emissions,
which entails very signifi cant impacts to global environmental health.












Search WWH ::

Custom Search