Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
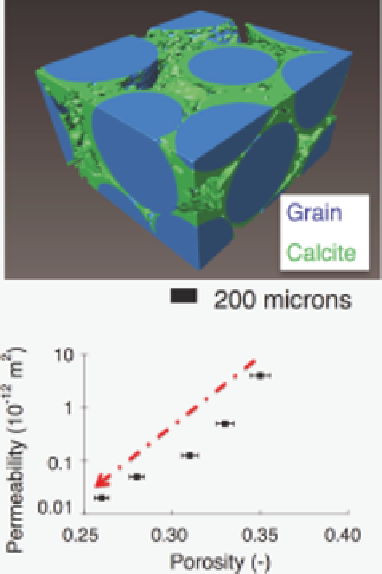
Figure 10.2.9
Calcite precipitation in a network of glass beads
Experimental results showing the correlation between porosity
and permeability
k
during calcite precipitation in a network of glass beads. The top fi gure shows an X-ray
computed tomography image of a portion of the porous medium. The lower fi gure
shows that a porosity decrease of
Φ
30% causes a permeability decrease of about two
orders of magnitude.
Figures reproduced from Armstrong and Ajo-Franklin
[10.8],
with
permission from John Wiley and Sons.
∼
the heterogeneity of rocks (for example, the layered structure of many
sedimentary rocks would tend to attenuate the effect of weathering on
fracture permeability in the direction normal to the bedding [10.9]), and
other phenomena such as nanoparticle transport and aggregation
(clay minerals, in particular, can disproportionately affect permeability,
probably because of their nanoparticulate nature and high surface
area [10.12]).












Search WWH ::

Custom Search