Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
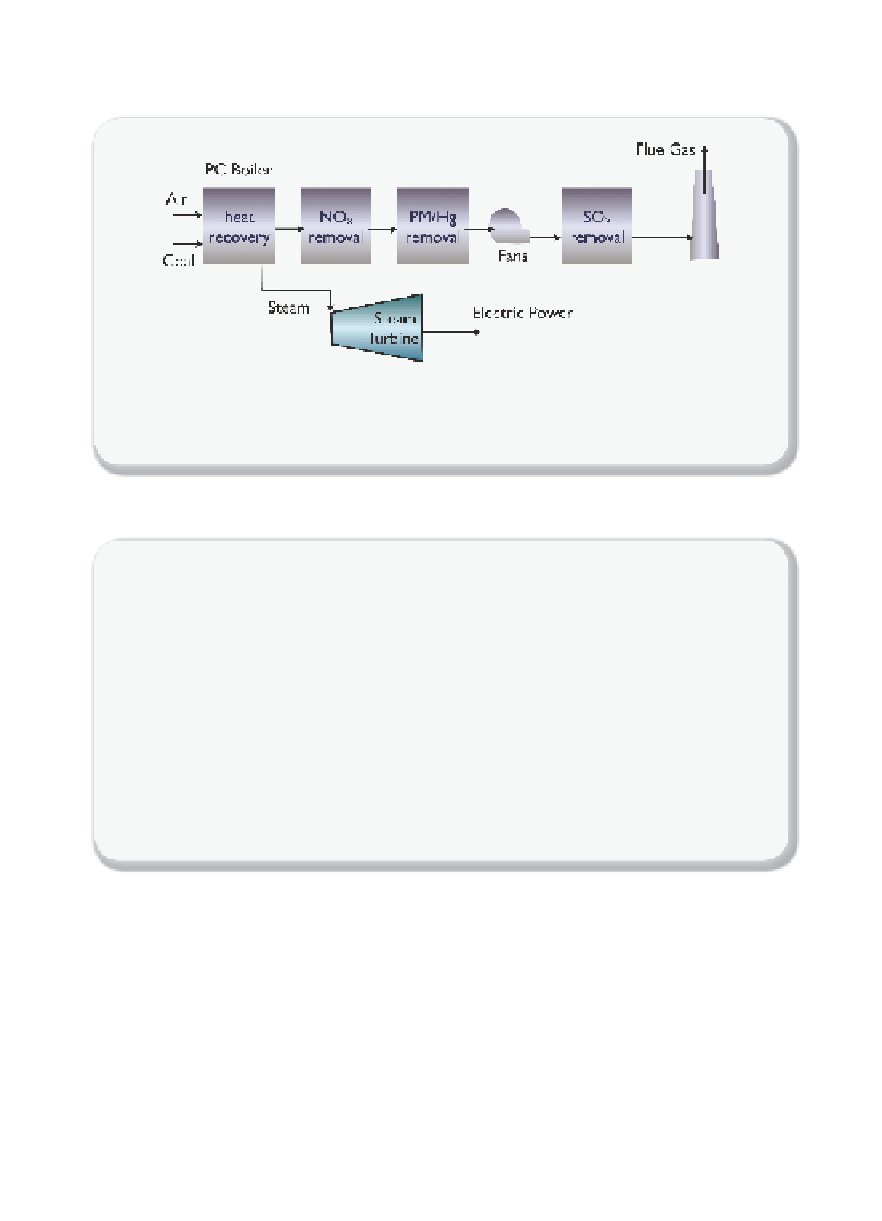
Figure 4.1.1
Coal-fi red power plant
This animation can be viewed at
: http://www.worldscientifi c.com/worldscibooks/
10.1142/p911#t=suppl
Box 4.1.1
Effi ciency of a power plant
Elementary thermodynamics states that the maximum effi ciency with which heat can
be transferred into work is given by the Carnot Effi ciency:
T
−
T
steam
cool
η
=
Carnot
T
steam
where
T
steam
is the temperature of the high pressure steam (550-600°C, or 823-873 K)
and
T
cool
(~40
C, or 313 K) is the temperature of the fl ue gas. In addition to the theo-
retical Carnot effi ciency, one has to take into account that a typical gas turbine has an
effi ciency of 75%. These are two important factors that explain why the maximum
thermal effi ciency of existing coal-fi red power plants is about 44%.
°
CO
2
for geological storage because CO
2
needs to be compressed (typi-
cally to 150 bar) for easier transport. Clearly, the energy used for the cap-
ture and compression of CO
2
will reduce the effi ciency of a power plant.
So to summarize, the main advantage of post-combustion carbon
capture is that it can be added on as an accessory to an existing power
plant without requiring the construction of an entirely new plant. The main
drawbacks are the reduction of energy production for the power plant,
and the fact that the size of such a separation unit can be signifi cant —
too big, even, to easily fi t on the power plant site.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search