Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
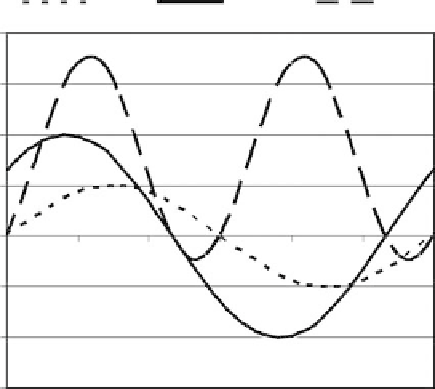
Volts
Current
Power
8.0
6.0
4.0
2.0
0.0
-2.0
-4.0
-6.0
Time
FIGURE 7.5
Instantaneous power in an arbitrary AC circuit.
The average power is found by integrating over one cycle:
V
PP
cos
2
F
P
avg
However, what is measured for AC circuits are average values of current and voltage, which are
given by the root mean square values:
V
(
v
v
)
0.5
{
V
p
sin (
qt
)
V
p
sin (
qt
)}
0.5
V
p
/2
0.5
0.707
V
p
However, that is for single-phase. For three phases, the measured current is reduced by 3
0.5
. So, for a
three-phase transfer of power, each leg is transferring a current equal to the (coil current)/1.73, and
therefore the wire size needed is smaller. The real power generated or consumed is given by
P
avg
VI
cos
f
(7.14)
where cos
f
is the power factor. Adding a number of induction generators to the utility line can
change the power factor and reduce the actual power delivered, a concern of the utility company,
since the utility grid supplies the reactive power for the induction generators. Therefore, some wind
turbines and most wind plants have capacitors added to the wind turbine or to the electric substation.
There are a number of electrical conversion systems for wind turbines [1-8].
7. 2 G E N E R ATO R S
The main classifications of generators are direct current, synchronous, and asynchronous generators
(subdivided into induction generators and permanent magnetic alternators). The operation is constant
or variable rpm, and as noted, the constant-rpm operation only reaches maximum power coefficient
at one wind speed (
Figure 6.13
). The variable-rpm operation up to the rated wind speed is along
the line of maximum power coefficient (
Figure 5.11
); however, above that wind speed not all the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search