Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0
1
23456 789
10
Speed Ratio
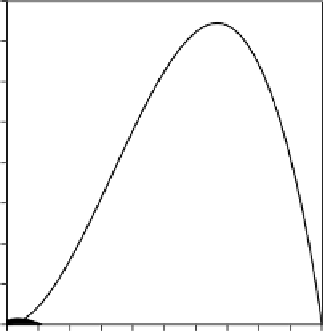
FIGURE 6.4
Comparison of power/area for a translating drag device (small solid curve) and a translating lift
device versus speed ratio of the device to the wind.
and the value of the axial interference factor is substituted into the equation to obtain the power/
area for a lift device:
P
A
3
RAA
2
0.5
v
4
(
1
)
(6.20)
0
A lift device can produce much more power per area of blade than a drag device (Figure 6.4).
Notice the small black line is for the drag device, which reaches a maximum of around 0.22 at a
speed ratio 0.3. The maximum for the lift device is around 15 at the speed ratio 2/3 of the ratio of
lift to drag coefficients. For this example, the power per area of blade was calculated for the drag
device with a drag coefficient of 1.5, and for the lift device, the ratio of lift coefficient to drag coef-
ficient was 10. Thus, the lift device can easily produce fifty times the power per blade area—another
reason drag devices are not used to produce electricity, although a company in South Africa has a
farm windmill that has an option for an electric generator.
6.5.1 M
AXIMUM
T
HEORETICAL
P
OWER
The maximum power/area can be found by plotting the curve
P/A
versus
]
(Equation 6.20) or by
using calculus. The answer is
]
1/3 or 1. Of course,
]
1 means that there is no reduction of wind
speed and the disk does not take out any power. For
]
1/3, the maximum power is
P
A
16
27
3
0.5
R
v
(6.21)
0
Therefore, the maximum power coefficient, from Equation 6.6, is
C
P
16/27 0.59. Real rotors
will have smaller power coefficients due to drag, tip and hub losses, losses due to rotation of the
wake, and frictional losses; however, measured values can reach 50% (which includes drive train
and generator). This is another reason lift devices are used to generate electricity, compared to drag
devices, as the maximum theoretical power coefficients are 50% versus 20%. However, the farm
windmill, which has some of the same characteristics as a drag device (large solidity, low tip speed
ratio) is well designed for the application of pumping low volumes of water.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search