Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
occurring during the initial stages of operation
[183]
. Contrary to these observations, Callejas
et al.
[181]
reported a decrease in the nitrogen content in coke with time on stream for the
Maya heavy crude during the early stages of the experiment. This suggests that this coke was
rather “young”, still possessing some reactivity. But, the “young” coke, which is more soluble,
had more deactivating effect on HDS activity than less soluble coke
[184]
. Also, in area of
active phase, coke deposits were thinner than on the bare support
[185]
. For extrudates used in
hydroprocessing of several gas oils, typical M-shape profiles of coke were observed
[186]
.
This suggests that coke was deposited by sequential deactivation mechanism. It is then evident
that the observed trends in coke formation and its structure depend on the origin of crude, type
of catalyst and operating conditions. The time on stream at which the coke evaluation was
conducted is important as well. In the case of residues, metals deposited on the catalyst surface
during the operation may modify deactivating pattern by coke compared with distillate feeds.
For residues, the contribution of N-compounds to the overall deactivation will increase with
the progress of hydroprocessing, i.e., in the fixed-bed reactor, from the inlet towards the outlet.
4.3 Combined Effect of Coke and Metals on Deactivation
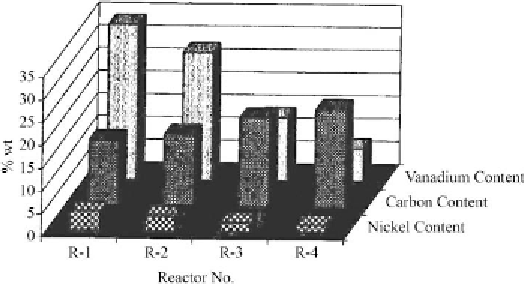
Multireactor systems have to be used for residues upgrading. For example, the ARDS process
discussed in
Chapter 3
has been used for the hydroprocessing atmospheric residue derived
from Kuwait crude. The extent of deposition of metals and coke in four reactors, which is a
part of the process, is shown in
Fig. 4.6 [12]
. In this case, the feed enters reactor 1 and
products exit reactor 4. As expected, the deposition of metals and associated deactivation
decreased from reactor 1 towards reactor 4, whereas reversed trend was observed for coke
deposition. The loss of pore volume and surface area exhibited similar trends as the coke
deposition (
Fig. 4.7
). This suggests that coke had a more detrimental effect on the pore volume
and surface area than metals. Similar set of catalysts as shown in
Figs. 4.6 and 4.7 [12,187]
Figure 4.6: Content of vanadium, nickel and carbon in spent catalysts from atmospheric residue
desulfurization (ARDS) reactors [From ref.
12
. Reprinted with permission].