Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 3.1: Properties of some distillate feeds and atmospheric residue [From ref.
44
. Reprinted
with permission].
Kerosene
Gas oil
Atmospheric residue
Density
0
.
7952
0
.
8967
0
.
978
Distillation (360+
◦
C)
IBP
89
232
50
202
363
90
262
424
FBP
291
440
Sulfur (wt.%)
0
.
45
2
.
29
4
.
2
Nitrogen (ppm)
200
800
2450
Asphaltenes (wt.%)
0
0
∼
4
CCR (wt.%)
0
0
∼
12
Vanadium (wt.%)
0
0
67
Nickel (wt.%)
0
0
20
CCR: Conradson carbon residue; IBP: Initial boiling point; FBP: Final boiling point.
residue. The consumption of catalyst increases with increasing severity as well. Consequently,
the amount of feed processed per unit weight of catalyst will decrease.
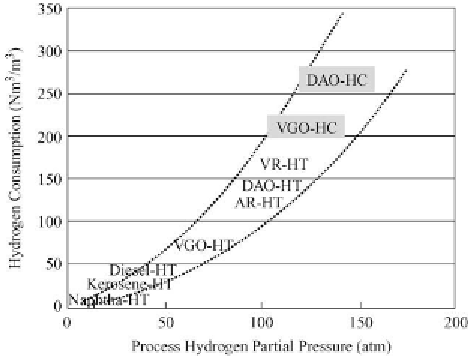
Figure 3.1
shows the
correlation between hydrogen consumption and hydrogen pressure. It is evident that much
more hydrogen is consumed during hydrocracking (HCR) than during hydrotreating (e.g.,
deasphalted oil-HC [DAO-HC] vs DAO-HT).
Figure 3.1: Effect of H
2
pressure and feed origin on hydrogen consumption.