Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
achieved by passing hot inert gas (e.g., N
2
or CO
2
) across the downflowing stream of spent
catalyst. This permits higher regeneration rates and reduced residence time. Stripping prior
regeneration improves temperature control and fluid properties of the catalyst.
A bag house for removing dust during regeneration is part of the TRP process (
Fig. 6.41
)
[471]
. To further ensure environmental acceptance, the dust free gas is then scrubbed to
remove SO
x
generated during the oxidation of sulfur in spent catalyst. Only after scrubbing,
the gas is released to the atmosphere. The scrubber solution is neutralized and then discharged.
The composition of the sludge removed from the scrubbing solution approaches that of
gypsum. Therefore, it is classified as a non-hazardous solid.
To provide complete service to petroleum refineries, the new XpresS presulfiding process was
added to the TRP process
[473]
. The catalyst presulfided using the former process exhibits a
high stability in air and its activity approaches that of the in-site presulfided catalyst. With this
catalyst, the start-up of the reactor operation was greatly accelerated without an isotherm being
observed.
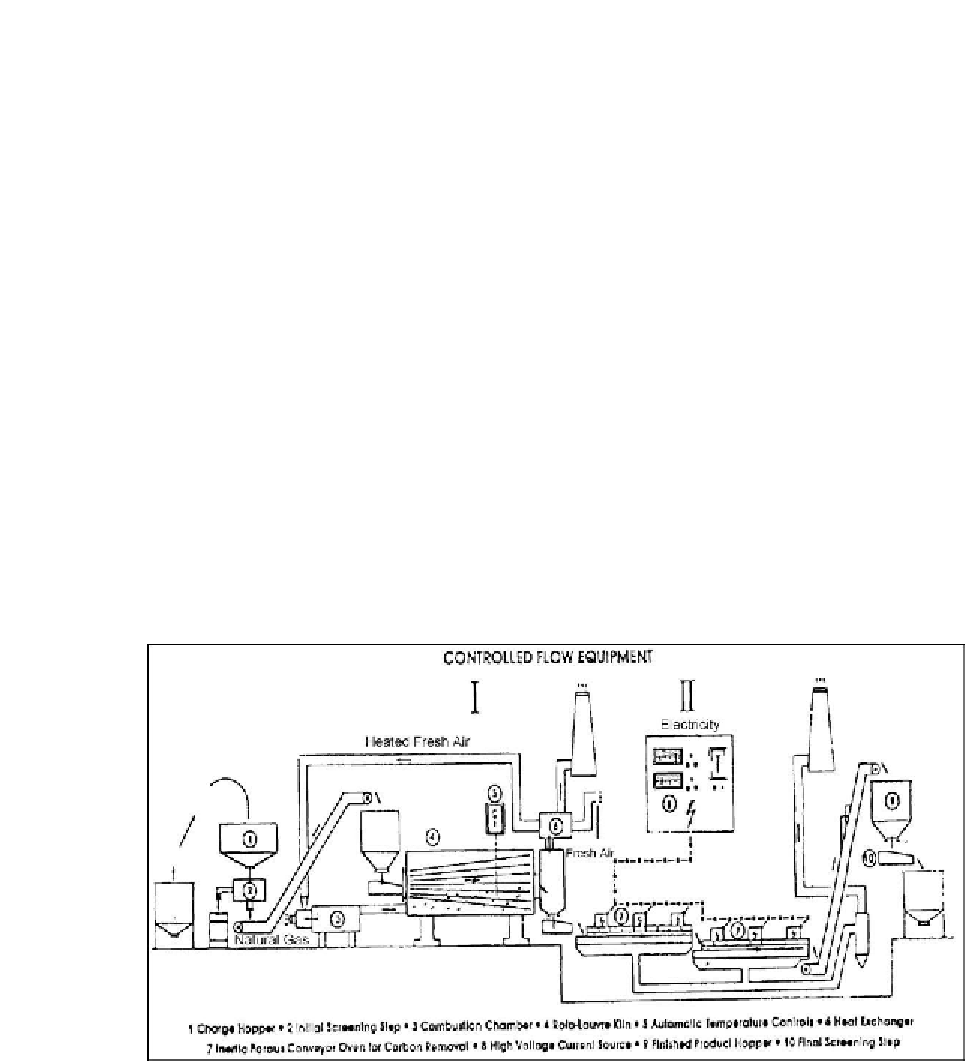
6.4.4.3 EUROCAT Process
The central part of the EUROCAT process shown in
Fig. 6.44 [448]
includes a continuous
rotolouvre, which is a sophisticated cylindrical drum rotating slowly on a horizontal axis and
enclosing a series of overlapping louvres. The louvres extend the full length of the drum
(
∼
11m) to form a conical inner shell, which increases in diameter toward the discharge end
Figure 6.44: Schematics of EUROCAT continuous off-site regeneration process [From ref.
448
.
Reprinted with permission].