Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
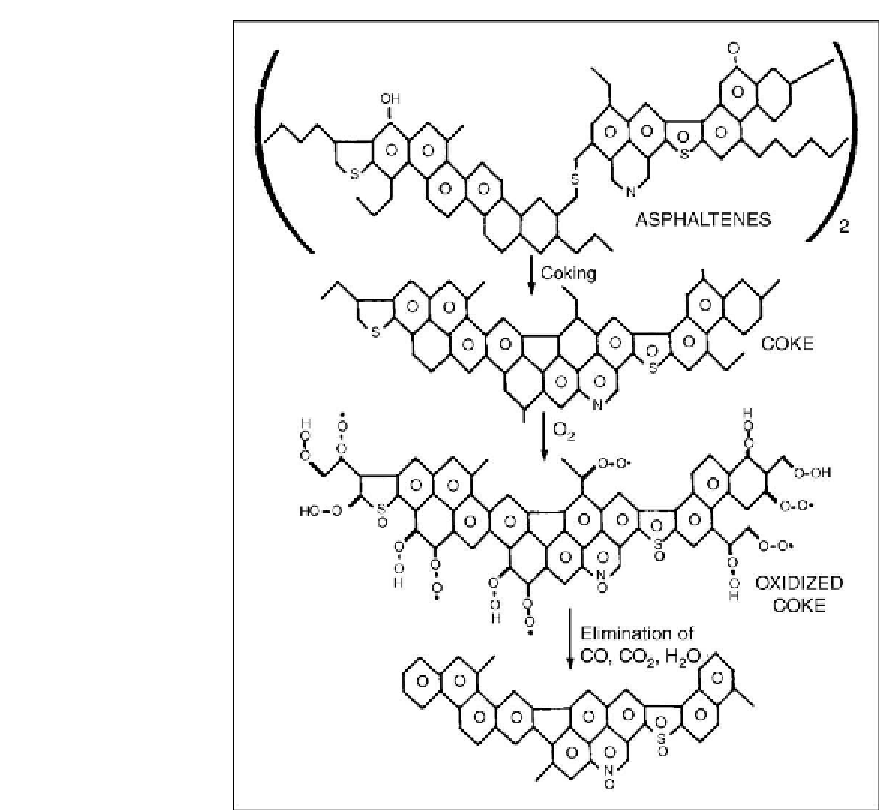
Figure 6.2: Mechanism of oxygenated complexes formation during auto-oxidation of coke
[From ref.
332
. Reprinted with permission].
measuring yields of H
2
O in similar manner as that of CO
2
and CO shown in
Fig. 6.3
.
Figure 6.4
shows that during the stepwise regeneration, most of the hydrogen was already
removed at 350
◦
C. At the same time, less than 20% of carbon was removed. It is believed that
most of this carbon originated from the oxidation of alkyl substituents and hydrocarbons
trapped in the coke, i.e.:
C
n
H
m
+
(
n
+
0.5
m
)O
2
=
n
CO
2
+
0.5
m
H
2
O