Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 2.9
The dependence on the electron energy for the diffusion cross section of electron
scattering by atoms of inert gases [34] according to measurements.
and satisfy the Schrödinger equations
H
H
ψ
D
ε
ψ
g
,
ψ
D
ε
ψ
u
,
g
g
u
u
where
H
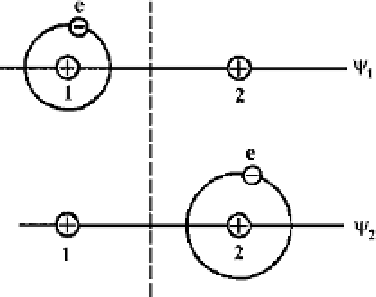
is the Hamiltonian of electrons. One can construct, say, the wave function
ψ
1
, if a valence electron is located near the first atomic core, as a combination of
the eigenstate wave functions as
1
p
2
(
ψ
D
ψ
C
ψ
u
).
1
g
We now assume the absence of transitions between states during evolution of the
quasimolecule when the distance between the colliding ion and atom varies. Then
theelectronwavefunctioninthecourseofvariationofanion-atomdistance
R
is
given by
2
4
3
5
Z
t
g
(
t
0
)
dt
0
„
1
p
2
ψ
ε
Ψ
(
r
,
R
,
t
)
D
g
(
r
,
R
)exp
i
1
2
4
3
5
.
Z
t
u
(
t
0
)
„
1
p
2
ψ
ε
dt
0
C
u
(
r
,
R
)exp
i
1
Here
r
is the electron coordinate, and we account for the wave function of a sta-
tionary state is proportional to exp(
is the state energy. From this
formula we have for the probability of electron transition from one core to another
one [54]
i
ε
t
/
„
), where
ε
Z
t
Δ
(
R
)
2
2
sin
2
P
(
t
)
Djh
ψ
2
(
t
)
j
Ψ
(
t
)
ij
D
dt
,
„
1