Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Ta b l e 2 . 21
Parameters of radiative transitions involving the lowest excited states of helium and
argon atoms.
Δ
ε
is the transition energy,
λ
is the wavelength of an emitted photon, and
τ
r
is
the radiative lifetime with respect to this transition [149].
Radiative transition
Δ
ε
,eV
λ
,nm
τ
r
,ns
He(2
1
P
1
1
S
)
!
21.22
58.433
0.56
He(2
3
P
2
3
S
)
!
1.144
1083
98
He(2
1
P
2
1
S
)
!
0.602
2058
500
Ar(3p
5
4s
3
P
1
!
1
1
S
)
11.62
106.67
10
Ar(3p
5
4s
1
P
1
!
1
1
S
)
11.83
104.82
2
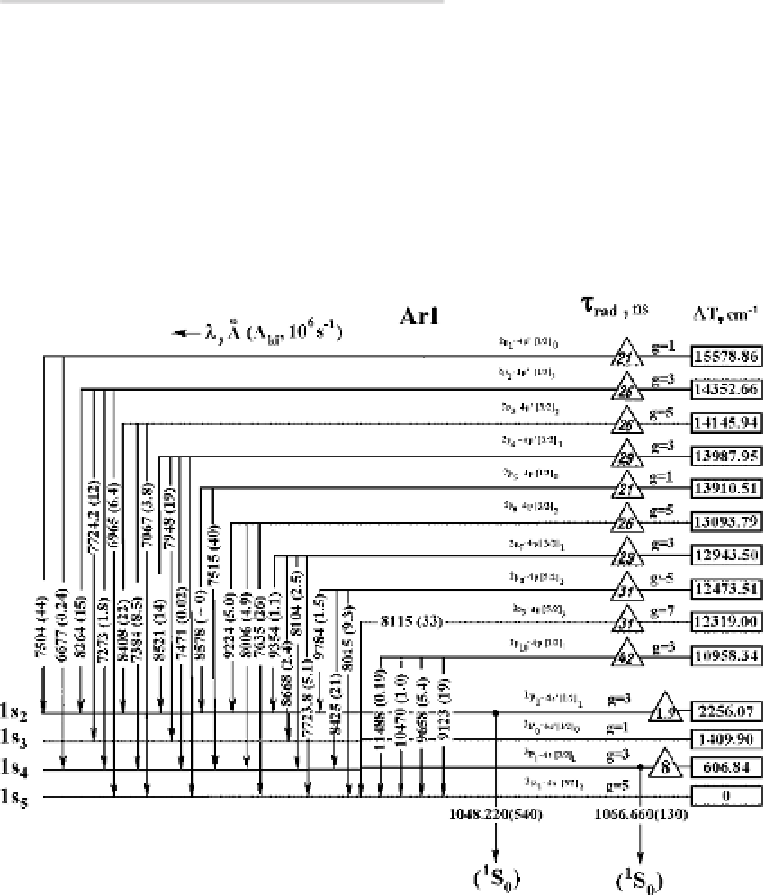
The radiative spectrum of an atom for excited states may have a complex form
because of various forms of interactions inside the atom. As a demonstration of
this, we represent in Figure 2.28 the radiative transitions of the argon atom, which
include the upper states of transitions where an excited electron is found in 4s
and 4p states.
T
is the excitation energy of states which energy is counted from
the lowest excited state, and
Δ
rad
is the radiative lifetime for a given excited state
that is summed over all transition states from this one, whereas
τ
τ
D
1/
A
ki
is
ki
Figure 2.28
Radiative transitions for the argon atom from states of the groups of 2s and 2p in
Pashen notation.