Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
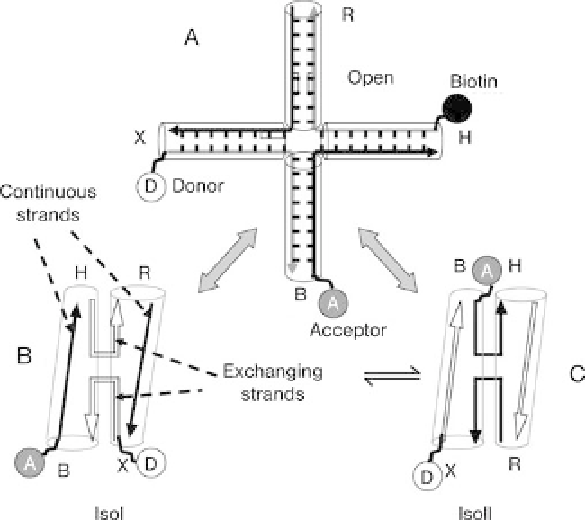
Figure 11.4 Open- and stacked-X structure of HJ. Two folded
forms (isoI and isoII) are expected to interconvert via an
unstacked intermediate resembling the unfolded open form.
Attaching dyes and biotin to various arms can provide information
on HJ conformations via FRET.
There are two alternative conformers [100, 105, 106] known as crossover isomers
(isoI and isoII, for example). The relative populations of these conformers were
determined using time-resolved FRET and NMR [121], and it was also shown that
these conformers interchange with each other [128
-
130]. Equilibrium populations of
the two conformers are determined by the junction sequence [105, 106, 121, 130] but
not by solution conditions [14, 131]. Therefore, it has not been possible to study the
stacking conformer transitions using bulk solution techniques which require syn-
chronization. Below, we will show that conformer transitions can be detected from
singleHJmolecules and their rates canbe determinedunder a variety of conditions. An
important question remains as towhether a non-migratableHJ is a goodmodel system
since HJs in vivo would mostly consist of homologous sequences that allow spontane-
ous branch migration in which the branch point can hop forward and backward in a
stochastic way. Our single-molecule approaches can measure structural properties
even in a migratable junction, allowing us to tackle these issues for the
first time.
11.4.2
Conformer Transitions of Non-migratable HJ
We assembled non-migratable HJs from four component strands of 22 nucleotides
each such that the four helical arms (B, H, R and X, see Figure 11.4 for nomenclature
convention) consist of 11 bp each. Three of the four helices were conjugated at the