Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
constant of 1.5 s
1
and that the second process involved the binding of the EGF
molecule with a rate constant 2.0
10
9
M
1
s
1
. Practically all of the dimeric binding
sites were formed by binding Rh-EGF from the solution. The association of two
binding sites by lateral diffusion and collision along the plasmamembrane was rarely
observed [9].
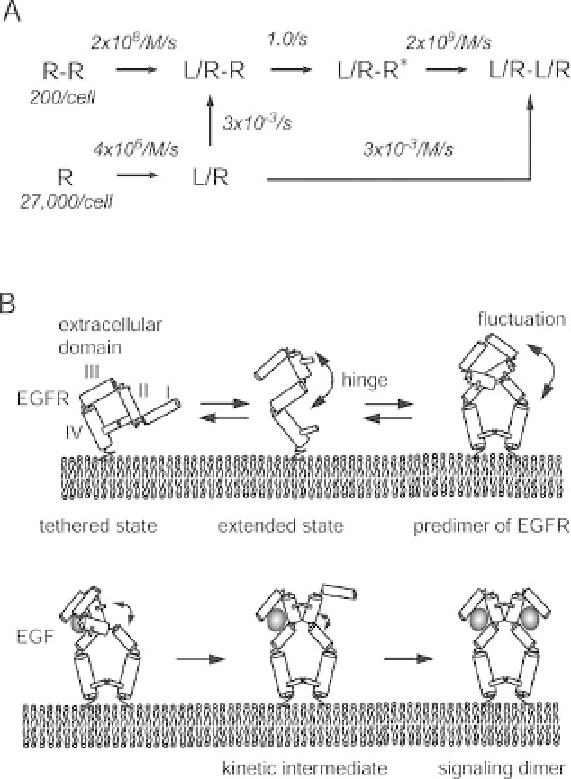
A simple reaction network for the formation of EGFR signaling dimers from
monomers and predimers of EGFR was constructed including the newly found
kinetic intermediate (Figure 5.3A). In this network, the intermediate is formed by a
conformational change of dimeric receptors after the binding of the
rst EGF
molecule. Solutions of the coupled differential equations for this reaction network
was obtained analytically and used to
fit the experimentally observed time course for
Figure 5.3 Amodel for the formation of signaling
dimers of EGFR. (A) The simplest schemes for the
formation of a signaling dimmer to explain the
experimental results. L and R represent ligand
(EGF) and receptor (EGFR), respectively. The
model includes the novel intermediate L/R-R
found using single-molecule analysis. The best
fit parameters obtained by this model are shown.
(B) A dynamic conformational change in the
predimer facilitates the formation of the signaling
dimer composed of EGF/EGFR complexes. See
text for details.