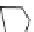Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Vertical switch
MOS gate electrode
Vertical signal line (
V
V
)
Light
SiO
2
n
+
PD
p
-well
n
+
Readout drain
V-sub
n
-sub
FIGURE 5.35
npn
-PD in MOS sensor pixel structure. (Reprinted with permission from Aoki, M., Ando, H., Ohba, S., Takemoto, I.,
Nagahara, S., Nakano, T., Kubo, M., and Fujita, T.,
Transactions on Electron Devices
, ED-29, 745-750, 1982.)
depleted. A bipolar transistor is made up of the PD,
p
-well, and
n
-sub, which play the roles of
emitter, base, and collector, respectively. By readout operation, the PD is set to video voltage
V
V
, which is positive voltage, and starts to integrate signal charges, reducing the PD potential.
When excess carriers are stored in the PD, its potential drops to negative voltage, correspond-
ing to the built-in potential (0.6 V) passing through 0 V. The
pn
-junction formed by the emitter
and base (PD and
p
-well) becomes a forward-biased condition, and additional excess charges
in the PD are emitted to the collector (
n
-sub) by way of the base (
p
-well). This means that cur-
rent flows from the collector (
n
-sub) to the emitter via the base. Blooming phenomenon is sup-
pressed by this mechanism in MOS sensors, while in the VOD structure of IT-CCDs, excess
charges are discharged to the
n
-substrate by depleting the
p
-well, as shown in Figure 5.18.
This works similarly to a static induction transistor (SIT). In the
npn
-PD, it works as a bipolar
transistor without depletion of the
p
-well. Therefore, the process of adjusting substrate voltage
at each sensor is not necessary in production, unlike in IT-CCDs.
It also should be pointed out that the
npn
-PD has the function to reduce sensitivity for far-
infrared light, which is excrescence for color image capturing, as discussed in Section 2.2.2.
Smear in CCD arises from the inflow of some part of generated charges or incident light
to the VCCD channel while potential wells move through from top to bottom in it. Smear
phenomenon also exists in MOS sensors, but the situation is a little different to that in
CCDs. In MOS sensors, one vertical signal line is connected to the readout drains of a num-
ber of vertical pixels. If some part of generated charges flow into the readout drains, they
are not distinguished from signal charges from PDs and are output together, that is, they
become smear charges. As the vertical signal line is reset to video voltage at every readout
operation of each line, smear charge integration period is one-line readout time. But all
readout drains connected to one vertical signal line contribute to smear phenomenon.
5.2.3 Progress in MOS Sensors
There has been some progress in MOS sensors, as follows.
5.2.3.1 Pixel Interpolation Array Imager
In the second generation of MOS sensors, the pixel interpolation array imager shown in
Figure 5.36 was developed.
23
The difference is that pixels are arranged with a half pixel