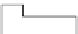Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
3.5 FDA Noise Reduction by CDS
Among the noise explained, kTC and 1/f noise can be removed or greatly reduced. While
the basic operation of an FD amplifier (FDA) was shown in Sections 2.3.1 and 2.3.2, its spe-
cific device structure and operation is explained by Figure 3.9.
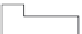
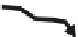
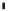
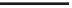
As shown in Figure 3.9a, the gate electrode input part of a source follower amplifier
(SFA) is directly wired with an FD to make up an FDA. It is operated using the following
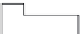
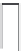
procedure, as shown in Figure 3.9b:
1. Potential of the FD reset to drain voltage
V
RD
is detected and output by the SFA.
2. Signal charge packet is transferred to the FD.
3. Potential of the FD containing the transferred charge packet is detected and out-
put by the SFA.
4. Reset operation to set FD to
V
RD
again by turning the reset gate channel to on-state
to accept the next signal charge packet.
At each step after step 4, the potential of the FD is not set to accurate
V
RD
, but varies
around
V
RD
because of reset noise, which is kTC noise caused by the reset operation, as
explained in Section 3.2. But the potential level of the FD can be detected by the SFA at
step 1, that is, the situation with no signal charge in the FD. And by taking the difference
between the SFA output at step 3, reset noise can be removed because the SFA outputs at
both steps have the exact same reset noise, that is, they are correlated. A representative cir-
cuitry to carry out this operation is a correlated double sampling (CDS) circuit, discussed
in Section 2.3.3, by making use of the correlation. Thus, a CDS is a circuit to obtain a “true
signal without noise” by subtracting (noise) from (true signal + same noise).
1/f noise
Drive transistor
V
dd
Source
follower
amplifier°
Load transistor
V
out
LG
Charge storage electrode
V
ss
Transfer electrode
(SFA)
Reset transistor
SG
TG
φR
V
RD
n
+
n
+
FDA
(a)
Floating diffusion (FD)
Signal charge
Reset drain
Reset noise
1. Output of reset
FD potential
2. Signal charge
transfer to FD
Signal charge
3. Output of charged
FD potential
4. FD reset
(b)
FIGURE 3.9
Operation of FDA and generation of reset and 1/f noise: (a) configuration; (b) operational sequence of FD.