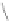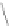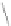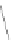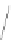Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Time Domain (1-D)
Space Domain (2-D)
(Temporal noise)
Circuit noise
Transistor noise
RTN
Random noise
Optical shot noise
Synchronous noise
Pixel characteristic variation
RTN
Fixed-pattern noise
FIGURE 3.1
Classification of noise in image sensors.
S
0
: true value
t
s
(
t
): real output overlapped with noise
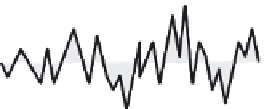
FIGURE 3.2
Signal overlapped with noise and the true signal value along a time axis.
As the amplitude of noise is represented by its difference from a true value, the noise
amplitude
N
is shown as
()
−
Ns ts
=
0
2
()
−
=
st s
(3.2)
0
In the case of a complete random temporal noise, the average value 〈
N
〉 is zero as follows:
()
−=
Ns ts
=
0
(3.3)
0
The summation of a number of uncorrelated noises is expressed as follows:
∑
N
total
=
N
i
i
2
∑
=
N
i
(3.4)
i
Using Equation 3.3, Equation 3.4 is rewritten as follows:
∑
2
N
total
=
N
i
(3.5)
i