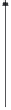Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
V
j
n
+
SiO
2
p
FIGURE 2.6
Cross-sectional view of
pn
-junction.
(a)
V
J
n
p
(b)
Bottom of conduction band
E
F
n
-type
p
-type
Top of valence band
Bottom of conduction band
(c)
V
B
ermal equilibrium
V
J
= 0 V
or open
E
F
Top of valence band
V
B
: Built-in potential
Depletion layer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
---
---
---
---
---
---
(d)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
++++
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
+
+++
: Electron
: Hole
+
-
: Ionized donor
: Ionized acceptor
-
+
n
-type
p
-type
FIGURE 2.7
Potential distribution model of
pn
-junction in thermal equilibrium: (a) model structure; (b) band diagram in
separated situation; (c) band diagram of
pn
-junction; (d) spatial distribution in
pn
-junction.
doped into a part of the
p
-type semiconductor area. In contrast, doping high-concentration
p
-type atoms into an
n
-type semiconductor area is also possible.
Although both
n
-type and
p
-type impurity atoms are distributed in the doped area, the
type having the higher concentration determines the polarity of conduction of the area,
because electrons occupy the states from the lowest to highest in energy space.
Using the model in Figure 2.7a, which shows
n
-type and
p
-type regions are directly
connected in real space, we show how energy distribution or potential distribution is