Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Analog value in seven
dimensions
Incident light intensity
at digitized coordinate points
S
(
r
k
,
c
l
,
t
f
)
(
i
,
r
, λ,
t
)
Continuous distribution
of four factors
A set of light intensity information
at built-in coordinate points
i
: light intensity
r
: space
S
: signal charge quantity
r
k
: pixel address
digitized
coordinate point
c
l
: color
t
f
: frame
Pixel
λ: wavelength
t
: time
t
t
x
x
y
y
∆
t
(exposure period)
∆
y
(a)
(b)
∆
x
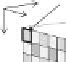
FIGURE 1.9
Comparison of optical image distribution with the image signal captured by image sensors: (a) optical image;
(b) image sensor signal.
c
c
R: coordinate
plane
R: coordinate
plane
G: coordinate
plane
G: coordinate
plane
B: coordinate
plane
B: coordinate
plane
r
r
t
t
(a)
(b)
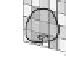
FIGURE 1.10
Digitized coordinate points: (a) digitized general coordinate points in a color system with an RGB color filter;
(b) digitized coordinate points in a single-sensor color system with an RGB color filter.
pixel number in the image sensors, three in the case of the three primary colors system
using RGB and the number of frames, respectively. Since the color signal at the coordinate
point
r
k
contains only one color information of three in a single-sensor color imaging sys-
tem, only one-third of the information is captured in (
r
,
c
,
t
) space, as shown in Figure 1.10b.
As the three color signals of RGB at each pixel are necessary to reproduce a color image,
the two color signals missing in the system are estimated by signal processing such as
demosaicking (color interpolation) using the correlation with the measured signal, as will
be discussed in Section 8.2.3.
While the signal of almost all image sensors is light intensity information at digi-
talized coordinate points, as shown in Section 1.2.3 by
S
(
r
k
,
c
l
,
t
f
), different types of digi-
tized coordinate points are possible. For example, as will be seen in Sections 5.3.3.2.3
and 7.3.2, there are sensors whose signal is time
T
, at which the change of light intensity
information reaches a predetermined amount as
T
(
f
(
i
),
r
k
), where
f
(
i
) is a function of light
intensity
i
.