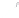Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Light source
Display
Signal
processing
Optics
Image sensor
Storage
Electrical image signal
CDS
AGC
Object
Colorization
ADC
Raw data
RAW
converter
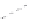
FIGURE 8.1
Overall flow of imaging system. AGC, automatic gain control.
Light source
Optics
Optical LPF
Lens
IR-cut filter
Intensity noise
Intensity noise
Shading
Flare
Flicker noise
optical shot noise
MTF
Space noise
Space noise
Distortion
aberration
Focusing
Cutoff freq.
Diffraction
(Airy disk)
Camera shake
Reflectance
Object
Wavelength noise
Wavelength noise
Spectral
response
Chromatic
aberration
FIGURE 8.2
Image information and elements of quality: light source and optics.
Spurious resolution around the Nyquist frequency and cross talk of light or signal charge
between pixels are also space noise. While the space range is determined by the area size
of the image, it also depends on the focal length of the lens. Wavelength noise includes
false color due to periodic space sampling, spectral response of the color filter, cross talk
of light and signal charge, and overlap between color filters. However, because the spectral
response of the color filter is decided by a balance of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), color repro-
ducibility, resolution, arithmetic load, and so on, this cannot be said as a rule. Wavelength
range is the color-reproducible area and depends on the number of filter colors and the