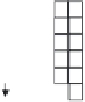Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
register. By repeating this action, five-by-six frame memories are filled. This operation is
continued until the desired phenomenon is observed. During the operation, when the signal
charges are transferred in parallel from the serial-parallel register to the parallel register, five
signal charge packets in the last row in the parallel register of the pixel above are transferred
to the serial-parallel register of the lower pixel. At each transfer of new signal charges from
the PD to the serial parallel register in series, five signal charges transferred from the above
pixel memory are transferred to the dumping drain D in series too.
Since this sensor has a register that can store 30 signal charge packets at each pixel, the
number of frames of images that can be captured is 30. This is an issue of the range of time
information on the accuracy and range of the four factors mentioned in Section 1.1.
While this sensor was aiming to realize 10
6
fps, the accomplished frame rate was 3 × 10
5
fps
at the time of presentation at the conference. The
in situ
storage image sensor (ISIS)
12
was
devised following the advice that linear CCD-type memory should be employed to pursue
a higher frame rate.
11
This advice was based on an insight that the serial-parallel register of
the above sensor made this goal difficult to achieve, an idea almost impossible to conceive
for those who have never actually developed CCDs.
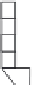
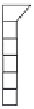
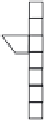
As shown in Figure 7.10, a linear CCD-type memory with 103 stages is formed at each
pixel and 10
6
fps is achieved. Signal charges under a photogate sensor are transferred to
the linear CCD memory at each 1 μs, and signal charges in the memory are transferred at
the same time, the head charge packet arriving at the drain is discharged. This operation
is repeated until the desired phenomenon is observed. In 2011, this sensor was improved
Photogate sensor
Linear CCD-type
memory
CCD switch
VCCD
Drain
FIGURE 7.10
Pixel configuration of ISIS (linear CCD-type frame memory). (Reprinted with permission from Etoh, T.,
Poggemann, D., Ruckelshausen, A., Theuwissen, A., Kreider, G., Folkerts, H., Mutoh, H. et al.,
Proceedings of IEEE
International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers
, 2.7, pp. 46-47, San Francisco, CA, 2002.)