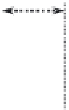Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
(FSI), is ongoing, as mentioned in Chapter 5. Noise reduction technologies, which are
important for signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) as sensitivity, are also still being developed,
as described in Chapter 5.
7.1.2 Dynamic Range
In this section, the DR, which is the range of light intensity information that a sensor can
capture, will be discussed. The DR is defined as the ratio of a signal electron number at
saturation level to that of dark noise, as shown in Figure 3.6. The DR is also defined as the
ratio of the maximum illuminance at which image information can be obtained without
saturation to the illuminance at which the SNR equals unity. In a linear system, since
a signal electron number is proportional to light intensity, both definitions of DRs are
in agreement. Because it is difficult to greatly improve the DR in a linear system using
state-of-the-art technology, a nonlinear system such as logarithmic conversion of photo-
current
1
or a combination of multiple images information is often employed. Nonlinear
systems have issues such as image lag, SNR, and temperature characteristics along with
complicated signal processing according to its applications, especially color applications.
Low-light performance should never be sacrificed for the sake of obtaining information on
highly illuminated objects.
The following sections discuss some examples of techniques that improve the DR.
Additionally, the pulse output sensor described in Section 5.3.3.2.3 is one of the methods
used to increase the DR.
7.1.2.1 Hyper-D CCD
Hyper-D CCD,
2
which was proposed in 1995, can transfer twice the conventional type of
signal charge packet number by forming double density VCCD, as shown in Figure 7.2,
to handle a short exposure signal along with a normal one. Saturated signals in normal
PD
Device saturation level
VCCD
Normal exposure signal
Normal exposure signal
Illuminance
(a)
Expansion
PD
VCCD
Synthetic pr
o
cessing
Device saturation le
v
el
Normal exposure signal
Short exposure s
i
gnal
(b)
Short exposure signal
Illuminance
FIGURE 7.2
Conceptual diagram of hyper-D CCD: (a) conventional CCD; (b) hyper-D CCD.